+1 (314) 370-6046 or
Contact Us - Argentina
- Australia
- Austria
- Bahrain
- Belgium
- Brazil
- Bulgaria
- Cameroon
- Canada
- Chile
- China
- Colombia
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Ecuador
- Egypt
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Hong Kong
- Hungary
- Iceland
- India
- Indonesia
- Iran
- Ireland
- Israel
- Italy
- Japan
- Kazakhstan
- Kuwait
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malaysia
- Malta
- Mexico
- Monaco
- Morocco
- Netherlands
- New Zealand
- Nigeria
- Norway
- Peru
- Philippines
- Poland
- Portugal
- Qatar
- Romania
- Russia
- Saudi Arabia
- Serbia
- Singapore
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- South Africa
- South Korea
- Spain
- Sri Lanka
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Taiwan
- Thailand
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- UAE
- United Kingdom
- United States
- Venezuela
- Vietnam

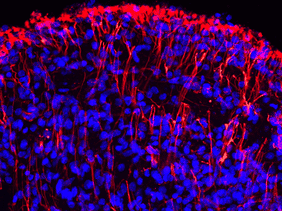
![Immunofluorescence - Anti-GFAP Antibody [2A5] (A104314) - Antibodies.com](https://cdn.antibodies.com/image/neuroscience/A104314_featured.png?profile=product_alternative_3)
![Immunohistochemistry - Anti-SOX2 Antibody [SOX2/1791] (A250002) - Antibodies.com](https://cdn.antibodies.com/image/neuroscience/A250002_featured.png?profile=product_alternative_3)
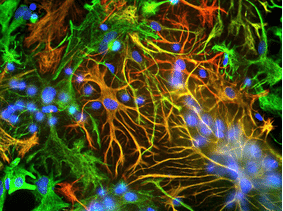
![Immunocytochemistry - Anti-Vimentin Antibody [VI-10] (A86652) - Antibodies.com](https://cdn.antibodies.com/image/neuroscience/A86652_featured.png?profile=product_alternative_3)
![Immunofluorescence - Anti-Nestin Antibody [4D11] (A85293) - Antibodies.com](https://cdn.antibodies.com/image/neuroscience/A85293_featured.png?profile=product_alternative_3)
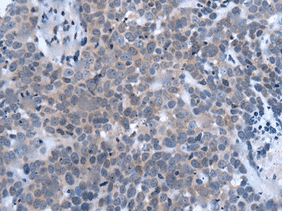
![Immunohistochemistry - Anti-PAX6 Antibody [PAX6/1166] (A249567) - Antibodies.com](https://cdn.antibodies.com/image/neuroscience/A249567_featured.png?profile=product_alternative_3)
![Immunohistochemistry - Anti-N Cadherin Antibody [8C11] (A248056) - Antibodies.com](https://cdn.antibodies.com/image/neuroscience/A248056_featured.png?profile=product_alternative_3)