Each quarter, Antibodies.com offers a travel grant up to $500 to help cover the cost of attending a conference. These travel grants are open to PhD candidates, post-docs and other research staff from academic research institutions in the US or Europe. The grant is intended to help cover the costs of registration, accommodation, and travel to a conference of choice.
For a chance to win, simply complete the application form below, including a summary of your research or abstract for the conference.
A team of our scientists will read all research summaries/abstracts that are submitted and select the winner based on which research they find most interesting. The winner of each quarter will be notified by email within the first two weeks of the subsequent quarter.
Dr Raffaele Sarnataro, University of Oxford
Thanks to the Travel Grant provided by Antibodies.com for covering a part of the costs of my participation in the annual Society for Neuroscience (SfN) meeting 2025, held in San Diego, California, from the 15 th to the 19 th of November 2025. I presented our work, “Mitochondrial origins of the pressure to sleep,” published earlier this year in Nature. Together with my colleagues in the Miesenböck research group, I studied a small group of sleep-regulating neurons in Drosophila and discovered that mitochondria play a central role in generating sleep pressure. My abstract was selected for an oral presentation in the SfN Nanosymposium “Sleep Regulation: From Molecular to External Factors,” which covered an impressively broad range of mechanisms influencing sleep.
Other topics included the contribution of potassium and calcium channels, metabolites produced by monoaminergic neurons, neural circuits underlying resistance to anaesthesia, and sleep-regulating (hypo) thalamic networks. Research on the circadian clock was also highlighted, spanning structural biology of core molecular machinery to calcium dynamics in regulatory brain centres. The questions and conversations following my talk were constructive and insightful, helping to clarify which aspects of this work are most intriguing for the broader neuroscience community.
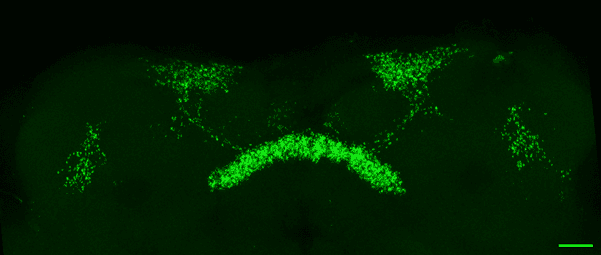
Maximum intensity projection of a fly midbrain where sleep-control dorsal fan-shaped body neurons, targeted by the R23E10-GAL4 driver line, have their mitochondria labelled with mito-GFP. Scale bar = 20 µm.
I was particularly pleased to see that several talks in my session featured Drosophila melanogaster research, which underscores the continued value of invertebrate models for uncovering fundamental principles of sleep biology. I found that the two other symposia in the SfN, on “Mitochondrial Dynamics and Energy Metabolism in Neurodevelopmental and Neuropsychiatric Disorders” and “Adenosine in the Brain”, further highlighted the growing interest in metabolism within neuroscience.
Elizabeth A. Cooper, CRUK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge
With the generous support of the Antibodies.com Travel Award, I attended the EMBO Workshop Adaptive Immunity in Barrier Tissue held in Basel, Switzerland, from 26th–29th August 2025. This meeting brought together leading researchers investigating immune regulation at barrier sites, providing an exceptional platform for scientific exchange and collaboration.
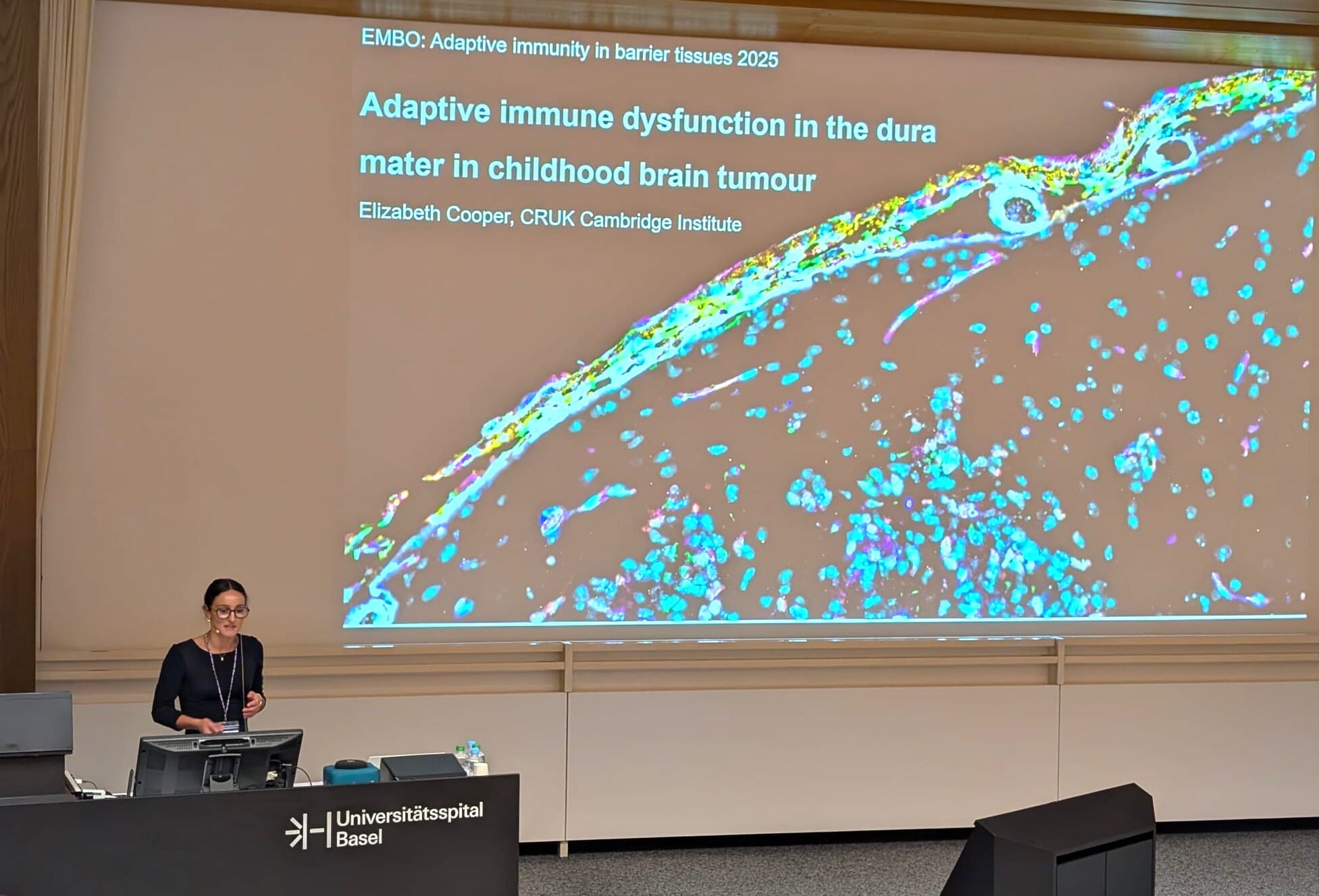
At the workshop, I presented my work as a talk entitled: “Adaptive immune dysfunction in the dura mater in childhood brain tumours.”
My project investigates how immune cells originating from calvaria bone marrow shape the tumour microenvironment in childhood brain tumours. The central nervous system (CNS) is no longer considered an immune-privileged site but is recognised as an active immunological organ, connected to peripheral immunity through meningeal lymphatic vessels (MLVs), the dura, and skull bone marrow niches. This interface integrates CNS-derived antigens into systemic circuits and is crucial for brain development, infection responses, and disease. A unique developmental feature is the delayed maturation of MLVs, which protects against premature inflammation but creates a window of vulnerability. I hypothesise that paediatric brain tumours exploit this period by co-opting adaptive immune programmes that normally establish CNS immune privilege, thereby fostering tolerance and immune evasion.
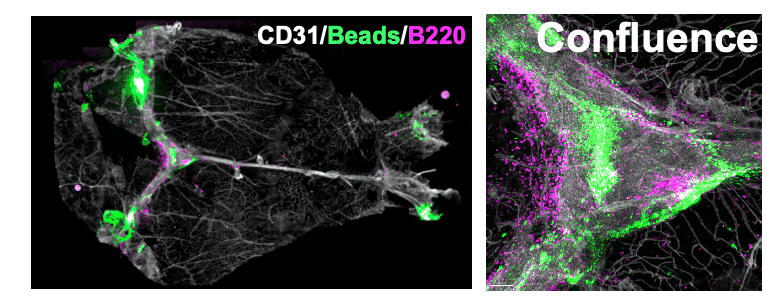
Confocal microscopy image of dura mater wholemount from a childhood brain tumour-bearing mouse. The bright green beads and surrounding magenta B cells reflect accumulation of antigens within the dura, suggestive of meningeal lymphatic dysfunction which could influence anti-tumour immunity.
Presenting at the EMBO workshop allowed me to share these ideas with experts in adaptive immunity and tissue-specific immunology. I received valuable feedback and identified potential collaborators, particularly in applying single-cell and spatial approaches to study brain–barrier immune interactions. I am deeply grateful to Antibodies.com for supporting my attendance at this outstanding meeting. The award was essential, and the experience will significantly shape the next steps of my research.
Ana Baião, I3S, University of Porto
With the support of the antibodies.com travel grant, I attended the NanoTME 2025 Conference in Enschede, Netherlands. This international meeting brought together researchers focused on nanomedicine and the tumor microenvironment (TME). I gave an oral presentation on my PhD project, which explores combining targeted nanoparticles with immune checkpoint blockade for colorectal cancer. My work centers on engineering polymeric nanoparticles to selectively deliver chemotherapeutics to tumor cells expressing specific surface markers, while modulating the immune microenvironment using checkpoint inhibitors. This dual strategy aims to enhance tumor drug accumulation and boost anti-tumor immune responses. Our results demonstrate improved drug delivery, immune activation, and therapeutic efficacy in preclinical models. My research lies at the intersection of targeted nanomedicine and immuno-oncology, with emphasis on overcoming therapeutic resistance in solid tumors.
Presenting my work enabled me to share findings, receive feedback, and exchange ideas with researchers addressing similar challenges. The scientific programme covered drug delivery, immunomodulation, and TME modeling. Sessions highlighted emerging strategies to overcome resistance and improve targeting and efficacy of nanoscale therapies. These talks offered insights directly relevant to the next steps of my research.
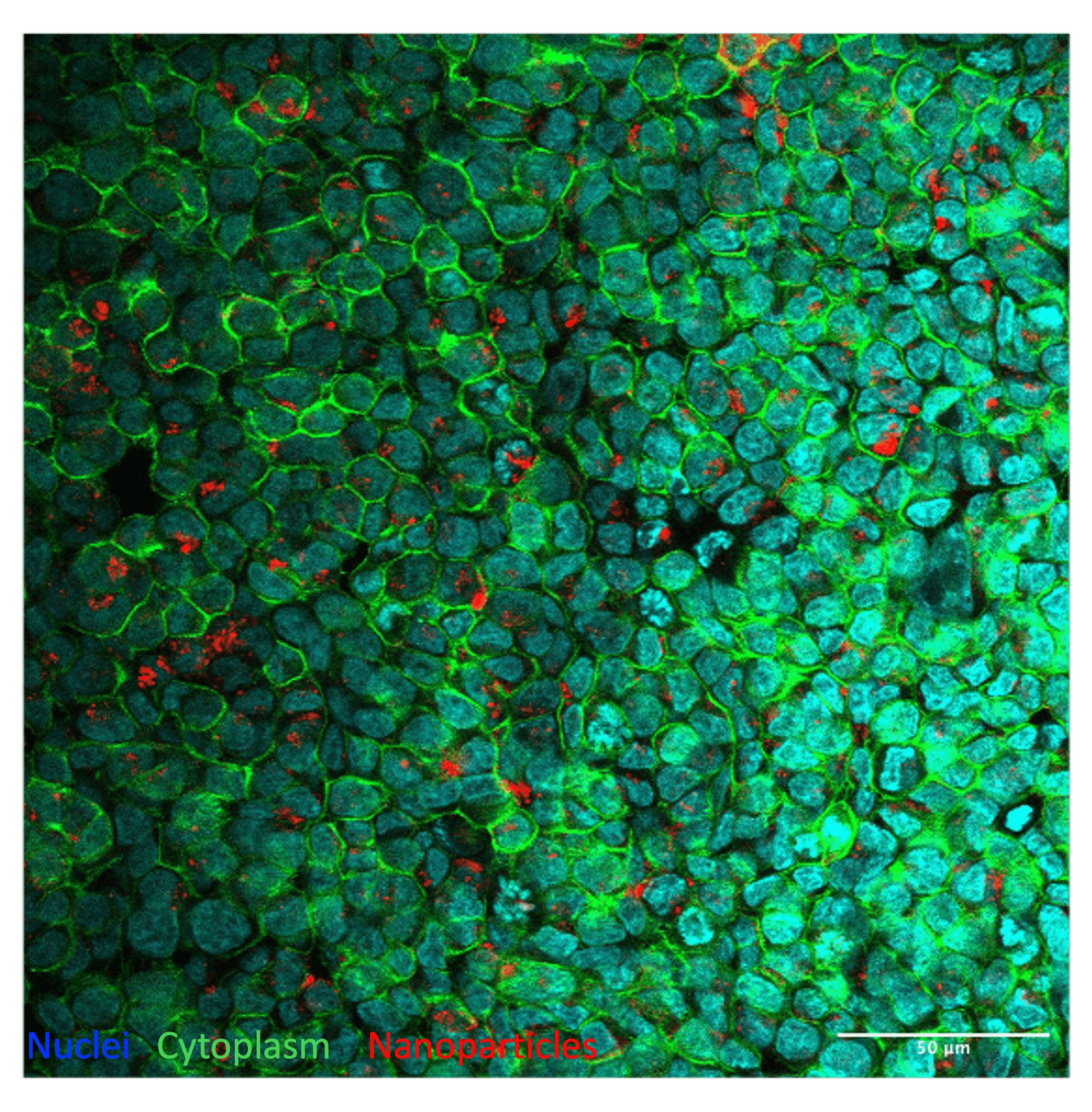
Confocal microscopy image showing selective uptake of CD44v6-targeted fluorescent nanoparticles (red) in a colorectal cancer cell line with confirmed overexpression of CD44v6. The pronounced intracellular accumulation reflects the specificity of the targeted nanocarrier system. Nuclei are stained in blue, and cytoplasmic membranes in green.
Beyond the scientific content, the conference was highly interactive. Since all sessions, meals, and social events were held at the same venue, it was easy to meet and speak with participants throughout the day. I connected with both early-career and senior researchers, broadening my perspective and expanding my professional network. Overall, attending NanoTME 2025 was a valuable experience that advanced my development as a researcher and strengthened the direction of my PhD work.
Isabel Elliott, University of Southampton
I was very grateful to receive a Travel Grant Award from Antibodies.com to attend the Keystone Symposia on Antibodies as Drugs: Innovative Formats, Design and Engineering in the beautiful snowy Keystone, Colorado from 17-21st February 2025. During the conference, I presented a short talk entitled ‘Structure-guided Disulfide Engineering Restricts Antibody Conformation to Elicit TNFR Agonism in Anti-cancer Therapeutics’ in a Symposia Spotlight session focussed on ‘Preclinical Development of Antibody Therapeutics: From Discovery to IND’. I also had the opportunity to present a poster during an evening poster session, where I was able to continue the conversations and discussions about my work. My talk and poster highlighted some of the research I have performed as part of my PhD, which is soon to be published in Nature Communications.
I work on immunostimulatory antibodies, which bind to co-stimulatory receptors, such as tumour necrosis factor receptors (TNFRs), expressed on immune cells. These antibodies aim to enhance the weak endogenous immune response towards tumours, for use as potential anti-cancer therapeutics. My project uses integrative structure-guided approaches, combining cancer immunology, X-ray crystallography, small angle X-ray scattering and molecular dynamics simulations, to engineer antibodies with enhanced agonistic activity.
Attending this meeting was a fantastic experience, allowing me to hear about the latest research in the design and engineering of novel antibody therapeutics across a range of different disease indications. I expanded my knowledge in a diverse collection of topics and had the chance to engage in interesting discussions with antibody engineering experts across both industry and academia. I was also able to meet some scientific collaborators of my research group, who are based outside of the UK, for the first time in person. The many opportunities throughout the conference to network and connect with fellow antibody scientists from across the globe will be hugely beneficial for my future scientific career. The conference has provided me with new perspectives for the last few months of my PhD and I am hugely thankful to Antibodies.com for helping to support my attendance.
Xiaoxue Han, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
I was honored to receive the Antibodies.com travel grant, which allowed me to attend the Chicago Bioengineering Conference (CBEC) 2024, where I presented my poster titled Hydrogel-based Exosome-Coated Oxygen Nanobubbles Enhances Wound Healing by Alleviating Hypoxia, Improving Angiogenesis, Suppressing Inflammation, and Reducing Scarring. My research aims to address critical challenges in non-healed wounds, including hypoxia, inflammation, and insufficient angiogenesis, which can severely delay recovery and impair patients’ life quality.
To overcome these issues, I developed a bio-adhesive polyvinyl alcohol/gelatin hybrid hydrogel dressing incorporating exosome-coated oxygen nanobubbles. Exosomes isolated from adipose-derived stem cell (ADSC)-derived mesenchymal stem cells can promote cell migration and angiogenesis, while reducing inflammation, due to the active therapeutic proteins and mRNA they carry. This approach not only alleviates tissue hypoxia but also enhances the targeted delivery of exosomes, promoting angiogenesis and reducing inflammation, ultimately leading to improved scarless wound healing outcomes in a full-thickness wound rat model. Further work will focus on different animal models, including the surgical incision wounds.
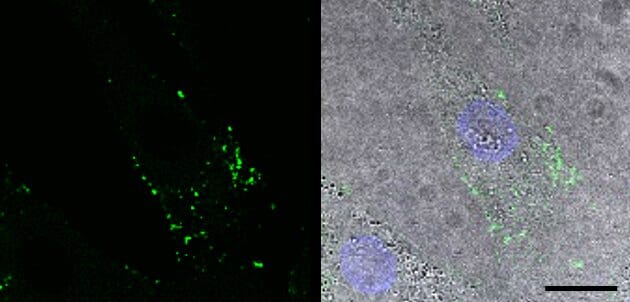
The intracellular uptake of Dio-labeled exosome-based nanoparticles in human dermal fibroblasts (HDF-a).
Attending CBEC 2024 gave me a valuable opportunity to showcase this work and engage in insightful discussions with experts in bioengineering and regenerative medicine. The experience has expanded my perspective on the potential applications of my research and provided important feedback that will help drive my future research studies. I am deeply grateful to Antibodies.com for their support, which made this rewarding experience possible and contributed to the advancement of innovative solutions in tissue engineering research.
Lara Hundsdorfer, University of Tübingen
Attending the ASCB/EMBO Cellbio2024 Conference in San Diego was an amazing experience, and I am incredibly grateful to Antibodies.com for supporting this journey with their travel grant. I had the exciting opportunity to present my work on our live-cell imaging-compatible cell stretching device in the session “Building Tissues Across Scales: From Micro to Macro”. Furthermore, it was great to exchange ideas with peers at the poster session about the second part of my project: The collective infected cell extrusion of bacterially infected epithelial cell monolayers via ERK activation waves. My research aims to uncover how mechanical stretch impacts the behavior and bacterial infection dynamics of epithelial cell monolayers.
The conversations and discussions with fellow researchers were not only insightful and inspiring but also provided valuable feedback and started potential collaborations for advancing these projects. The Cellbio2024 conference offered an incredible diversity of topics, which was ideal given the interdisciplinary nature of my work. Visiting numerous posters and attending many outstanding presentations provided fresh input and new information.
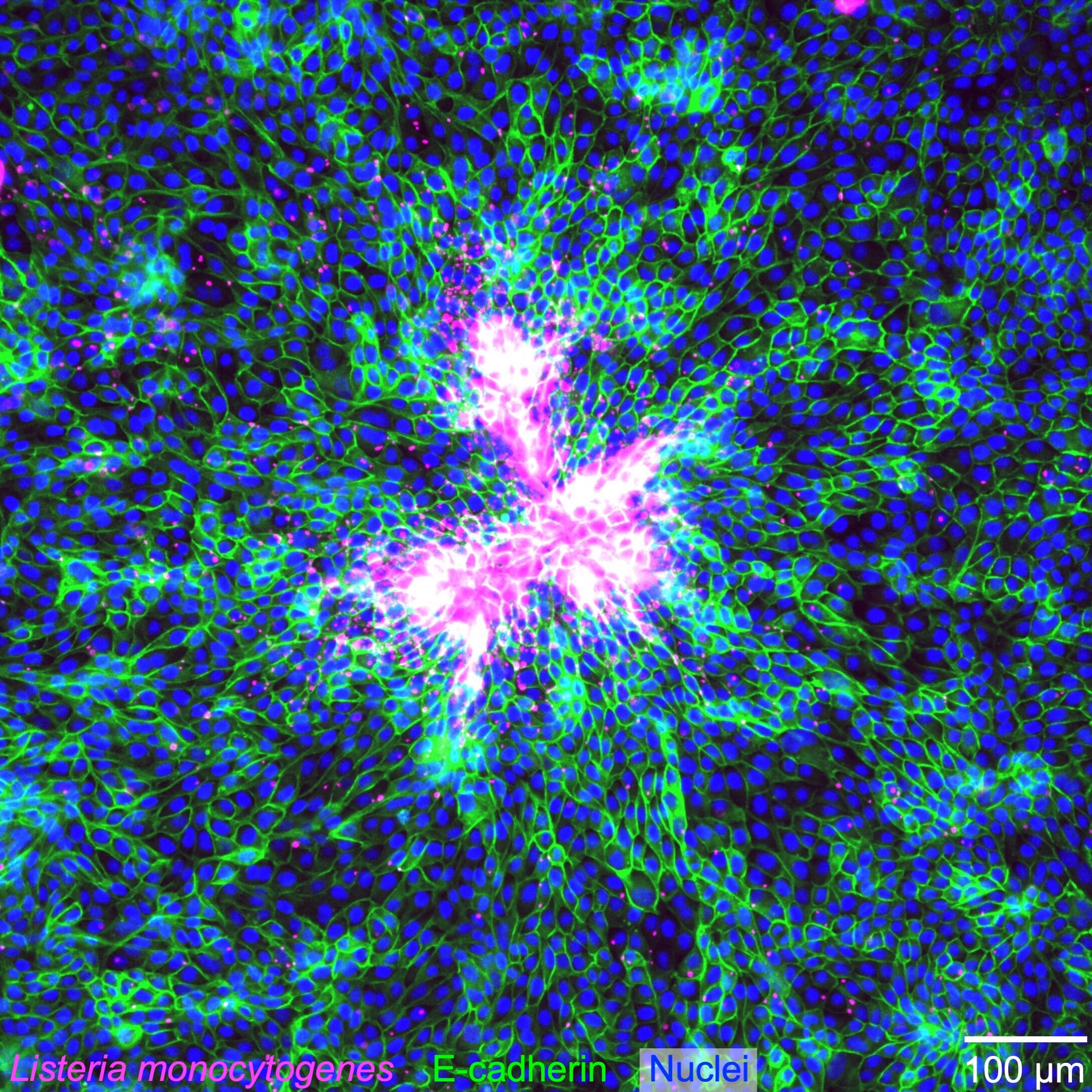
Collective extrusion of epithelial MDCK cells infected with the intracellular pathogen Listeria monocytogenes.
Participating in career development sessions, made this experience valuable for me on both a professional and personal level. Beyond the science, the conference was a great opportunity to network and connect with fellow researchers from around the globe. A special thanks to Antibodies.com for making this possible - allowing me to escape the grey German winter and enjoy the perfect combination of sunshine, science, and inspiration.