Biosimilar Antibodies
By Ryan Hamnett, PhD
Biosimilar antibodies are recombinant monoclonal antibodies that are identical in amino acid sequence to an antibody that has already been approved as a therapeutic, but have been produced in slightly different manufacturing processes or from different clones. Obtaining an original (reference) pharmaceutical-grade antibody is often expensive or impractical, so biosimilar antibodies are extremely useful in drug discovery and pre-clinical research for assay development and understanding disease mechanisms.
We offer over 700 biosimilar antibodies for research use which are greater than 95% purity, low endotoxin, and free from preservatives and carrier proteins.
Table of Contents
What are Biosimilar Antibodies?
Biosimilar antibodies are biological compounds or biologics, meaning they are made in living cells (usually mammalian cell lines) rather than being chemically synthesized. Due to unavoidable variation in biological production, biosimilars are therefore not perfect replicas of the original therapeutic. However, production of biosimilar antibodies uses highly reproducible recombinant DNA technology and the publicly available amino acid sequence of original therapeutic, resulting in a biosimilar that mimics the specificity, structure, function, efficacy and safety of the reference antibody.
Many biosimilar drugs are approved and used in clinical settings (see Biosimilars in Clinical Settings) as an effective but cheaper alternative to the reference product. Note that our biosimilar antibodies are for research use only (RUO) and are not approved for therapeutic use.
How do biosimilar antibodies differ from reference antibodies?
Biosimilar antibodies have demonstrated equivalency to the original reference antibodies. They bind to the same epitope on the target antigen, have the same sequence and structure, and show highly similar activity, efficacy, safety and immunogenicity profiles.
Nevertheless, variations in biologic production, including as a result of using different cell lines or purification processes, mean that biosimilars are not identical to reference antibodies. Glycosylation state, for example, is dependent on the cell type the biologic was created in. Interestingly, intentional modification of aspects such as the glycosylation state or small sequence adjustments to the Fc domain can improve on the original product by enhancing their effects or altering their pharmacokinetics, generating “bio-better” antibodies.1–3
While formulations between biosimilars and reference products can sometimes differ, Antibodies.com biosimilar antibodies are typically provided in a similar formulation to therapeutic products. Our biosimilar antibodies show comparable purity and monodispersity (see Biosimilar Antibody Quality Control), and include histidine and sucrose in their formulation to improve protein stability, buffer pH, optimize activity, and reduce aggregation.4
Biosimilar Antibody Quality Control
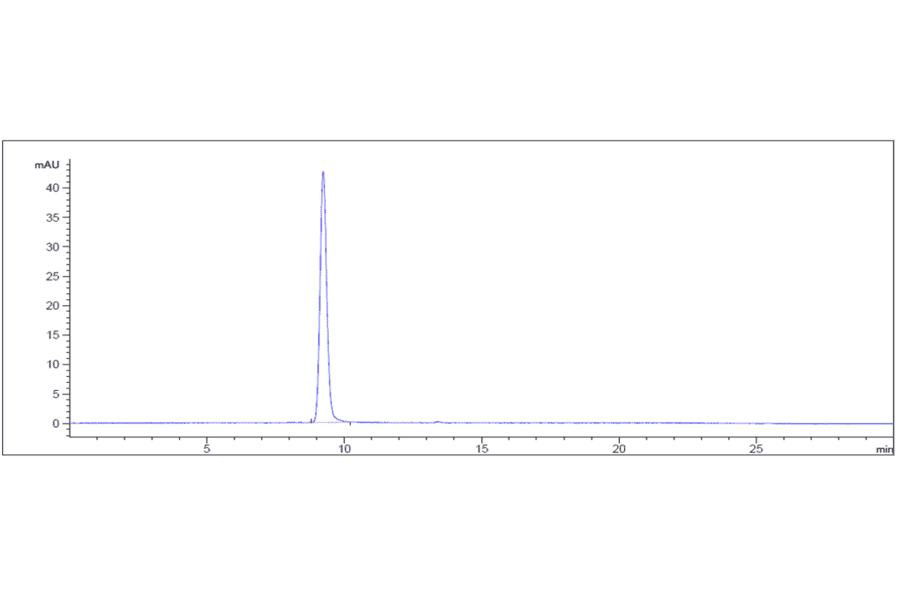
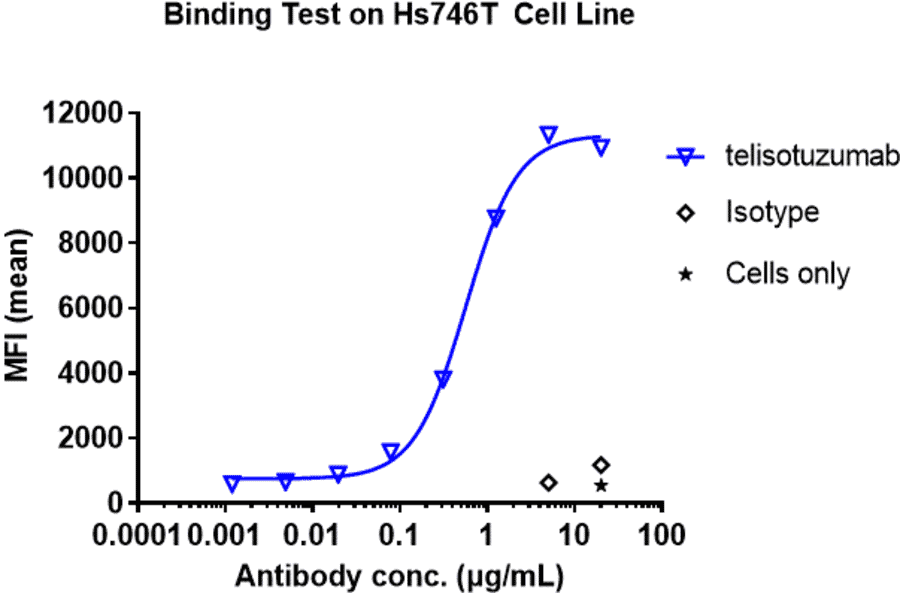
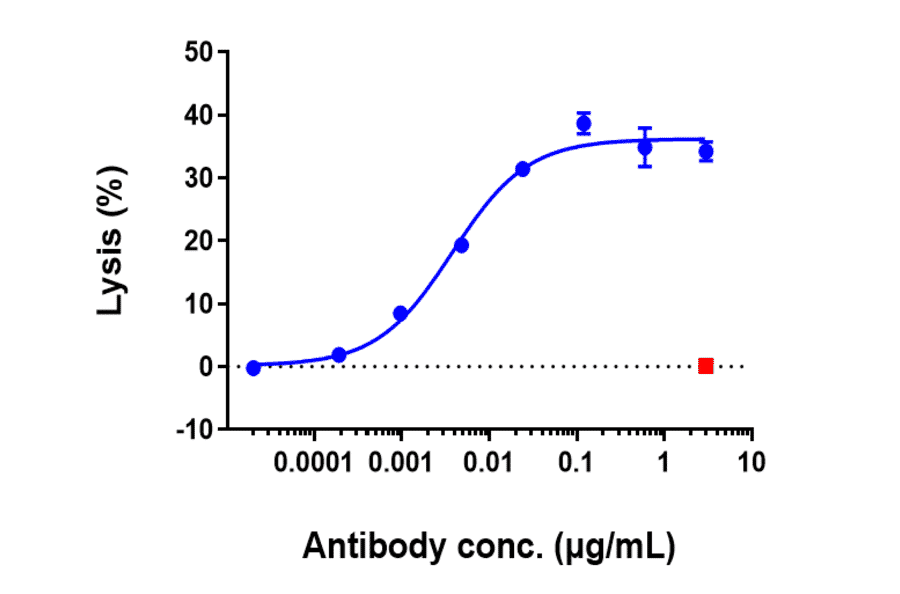
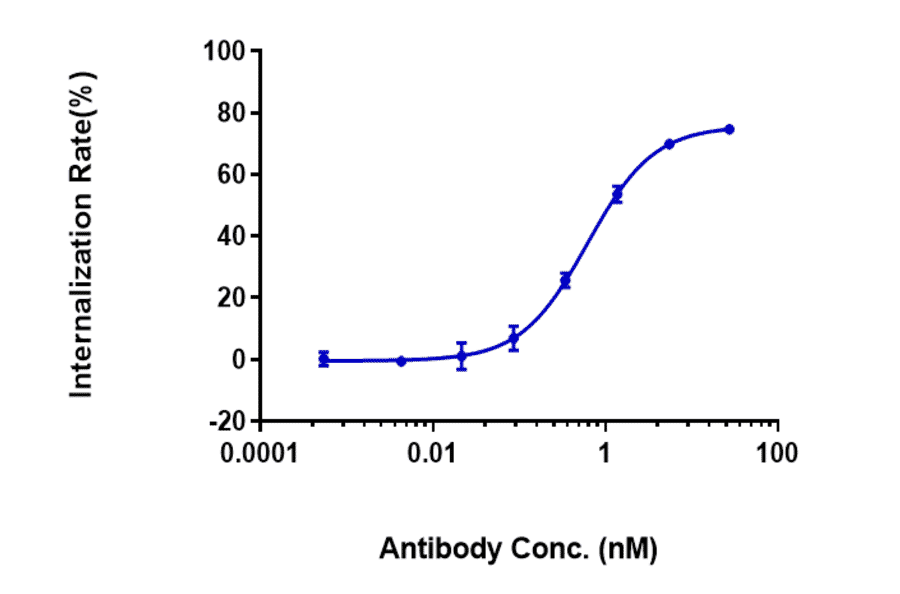
Antibodies.com biosimilar antibodies are routinely tested to ensure the highest possible quality and purity. Purity and monodispersity are assessed using both SDS-PAGE and size-exclusion high-performance liquid chromatography (SEC-HPLC), a gold-standard biophysical test that uses porous beads to separate molecules by size to enable easy visualization of any aggregates present in a sample. Our biosimilars also undergo extensive bioactivity testing, employing flow cytometry and ELISA across several antibody concentrations to establish binding affinity. Finally, our biosimilar antibodies are subjected to several assays to confirm optimal function. These include assays assessing internalization by endocytosis and ADCC, as well as in vivo assays relevant to the biological activity of the antibody, such as its ability to inhibit tumor growth.
Biosimilar Antibody Applications in Research and Drug Discovery
Biosimilars offer a cost-effective alternative to reference products, making them accessible for a broad range of research applications and aiding in rapid assay development. Critically, they serve as a source for a drug that may otherwise be too expensive to acquire, or else only available in large quantities. They can then be used for:
- Mechanistic studies: exploring the biological effects of existing therapeutics further
- Testing novel therapeutic approaches: modifying biosimilars and then performing efficacy studies in humanized disease models in mice
- Benchmarking new drugs: comparisons between new drugs and biosimilars for pre-clinical lead identification
- Understanding biophysical properties: using techniques such as surface plasmon resonance (SPR) to further characterize the stability, dynamics, structure and binding properties of therapeutic antibodies
- Understanding pharmacokinetic properties: How the drug is absorbed, metabolized and eliminated from the body, and how modifications may alter this
- Developing diagnostic assays: use biosimilars to optimize drug concentration, incubation time, dynamic range and validate its accuracy and reliability
Biosimilars in Clinical Settings
Though Antibodies.com biosimilar antibodies are available for RUO, biosimilar drugs have been available as outright therapeutics since 2006 in the EU, and 2015 in the US.5,6 Pharmaceutical manufacturers are able to make biosimilars once the patent of a reference product expires. Biosimilar drugs tend to be cheaper for patients and healthcare providers, but with the same function, safety and immunogenicity demonstrated following rigorous testing throughout the approval process.7,8
The FDA defines a biosimilar as having “no clinically meaningful differences from the reference product”.9 They can be used to treat the same conditions as the original reference product, and typically carry the same risks, but may be available at a lower cost.
~ Antibody Insights ~
In 2002, Humira was the first monoclonal antibody to be approved by the FDA in the US. Humira is the brand name of Adalimumab, which targets tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFα) and is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis. There are now 5 other versions (biosimilars) of Adalimumab: Amgevita, Hyrimoz, Idacio, Imraldi and Yuflyma.
Popular Biosimilar Antibodies
We offer over 700 biosimilar antibodies for research use in a wide variety of applications, including ELISA, FACS, functional assays and in vivo. Explore some of our most popular biosimilars below.
| Reference Product | Biosimilar | Reactivity |
| Adalimumab | Anti-TNF alpha Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rhesus Macaque, Cynomolgus Macaque |
| Alemtuzumab | Anti-CD52 Antibody | Human |
| Alirocumab | Anti-PCSK9 Antibody | Human, Mouse, Cynomolgus Macaque |
| Basiliximab | Anti-IL-2 Receptor alpha Antibody | Human |
| Brentuximab | Anti-CD30 Antibody | Human, Cynomolgus Macaque |
| Canakinumab | Anti-IL-1 beta Antibody | Human, Mouse |
| Cetuximab | Anti-EGFR Antibody | Human, Mouse, Cynomolgus Macaque |
| Daratumumab | Anti-CD38 Antibody | Human, Mouse, Cynomolgus Macaque, Rhesus Macaque |
| Denosumab | Anti-RANKL Antibody | Human, Cynomolgus Macaque |
| Eculizumab | Anti-C5 Antibody | Human, Mouse |
| Efalizumab | Anti-CD11a Antibody | Human, Rhesus Macaque |
| Gemtuzumab | Anti-CD33 Antibody | Human |
| Infliximab | Anti-TNF alpha Antibody | Human, Cynomolgus Macaque |
| Mepolizumab | Anti-IL-5 Antibody | Human |
| Nivolumab | Anti-PD1 Antibody | Human, Cynomolgus Macaque |
| Omalizumab | Anti-Human IgE Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rhesus Macaque, Cynomolgus Macaque |
| Palivizumab | Anti-RSV F Glycoprotein Antibody | Human, Cynomolgus Macaque, Mouse |
| Pembrolizumab | Anti-PD1 Antibody | Human, Cynomolgus Macaque |
| Rituximab | Anti-CD20 Antibody | Human, Cynomolgus Macaque |
| Sutimlimab | Anti-C1s Antibody | Human |
| Teplizumab | Anti-CD3 epsilon Antibody | Human |
| Tocilizumab | Anti-IL-6R Antibody | Human, Cynomolgus Macaque |
| Trastuzumab | Anti-ErbB2/HER2 Antibody | Human, Mouse |
| Vedolizumab | Anti-Integrin alpha 4 + beta 7 Antibody | Human |
References
- Moore, G. L., Chen, H., Karki, S. & Lazar, G. A. Engineered Fc variant antibodies with enhanced ability to recruit complement and mediate effector functions. mAbs 2, 181–189 (2010).
- Beck, A. Biosimilar, biobetter and next generation therapeutic antibodies. mAbs 3, 107–110 (2011).
- Zalevsky, J. et al. Enhanced antibody half-life improves in vivo activity. Nat. Biotechnol. 28, 157–159 (2010).
- Baek, Y., Singh, N., Arunkumar, A. & Zydney, A. L. Effects of Histidine and Sucrose on the Biophysical Properties of a Monoclonal Antibody. Pharm. Res. 34, 629–639 (2017).
- Raedler, L. A. Zarxio (Filgrastim-sndz): First Biosimilar Approved in the United States. Am. Health Drug Benefits 9, 150 (2016).
- Schiestl, M., Zabransky, M. & Sörgel, F. Ten years of biosimilars in Europe: development and evolution of the regulatory pathways. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 11, 1509 (2017).
- Biosimilar medicines: Overview. European Medicines Agency (2023).
- Eisenstein, M. Bring on the biosimilars. Nature 569, S2–S3 (2019).
- Biosimilars Basics for Patients. FDA (2024).