By Ryan Hamnett, PhD
ELISAs use antibodies to detect and quantify the amount of a target antigen in a liquid sample. Below are example protocols covering all the stages of multiple ELISA formats and assaying various types of sample for the detection of target proteins.
Following processing, all sample types should be aliquoted to minimize freeze-thaw cycles, and stored at -80°C.
Cell culture supernatant
Cell extracts
Tissue extract
Serum
Plasma
Other biological fluids (e.g. milk, saliva, urine)
Antigen coating
Blocking and standard preparation
Primary antibody incubation
Secondary antibody incubation (only for Indirect ELISA)
Detection and analysis
All sandwich ELISA plates sold by Antibodies.com come pre-coated with capture antibody, so the antibody coating steps of this protocol are not necessary to perform.
Antibody coating
Blocking and standard preparation
Sample incubation
Biotinylated antibody incubation
Biotinylated antibody incubation
Detection and analysis
All competitive ELISA plates sold by Antibodies.com come pre-coated with antigen or antibody, so the coating steps of this protocol are not necessary to perform.
Antigen coating
Blocking and standard preparation
Sample incubation with primary antibody
Competitive incubation
Secondary antibody incubation
Detection and analysis
All competitive ELISA plates sold by Antibodies.com come pre-coated with antigen or antibody, so the coating steps of this protocol are not necessary to perform.
Antigen coating
Blocking and standard preparation
Competitive incubation
Streptavidin amplification
Detection and analysis
Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)
Tris-buffered saline (TBS)
Cell and tissue extraction buffer
Bicarbonate/carbonate coating buffer (100 mM)
Purified antibodies are recommended to be diluted to 1-10 μg/ml, while unpurified antisera should be diluted to 5-20 μg/ml.
Wash buffer
Enzyme-conjugated secondary antibodies are recommended to be diluted to 20-200 ng/ml for colorimetric detection. This can be reduced to 10-100 ng/ml for chemiluminescence. Recommended dilution for streptavidin-HRP is 10-250 ng/ml. All recommendations are guides only; optimal dilution should be empirically determined.
Standard diluent
Note that ideally the standard diluent matches the sample matrix composition as closely as possible. For example, if the samples are from cell culture supernatant, culture medium should be used as the standard diluent. In instances where the sample matrix is impossible to replicate, such as serum, BSA is often used instead.
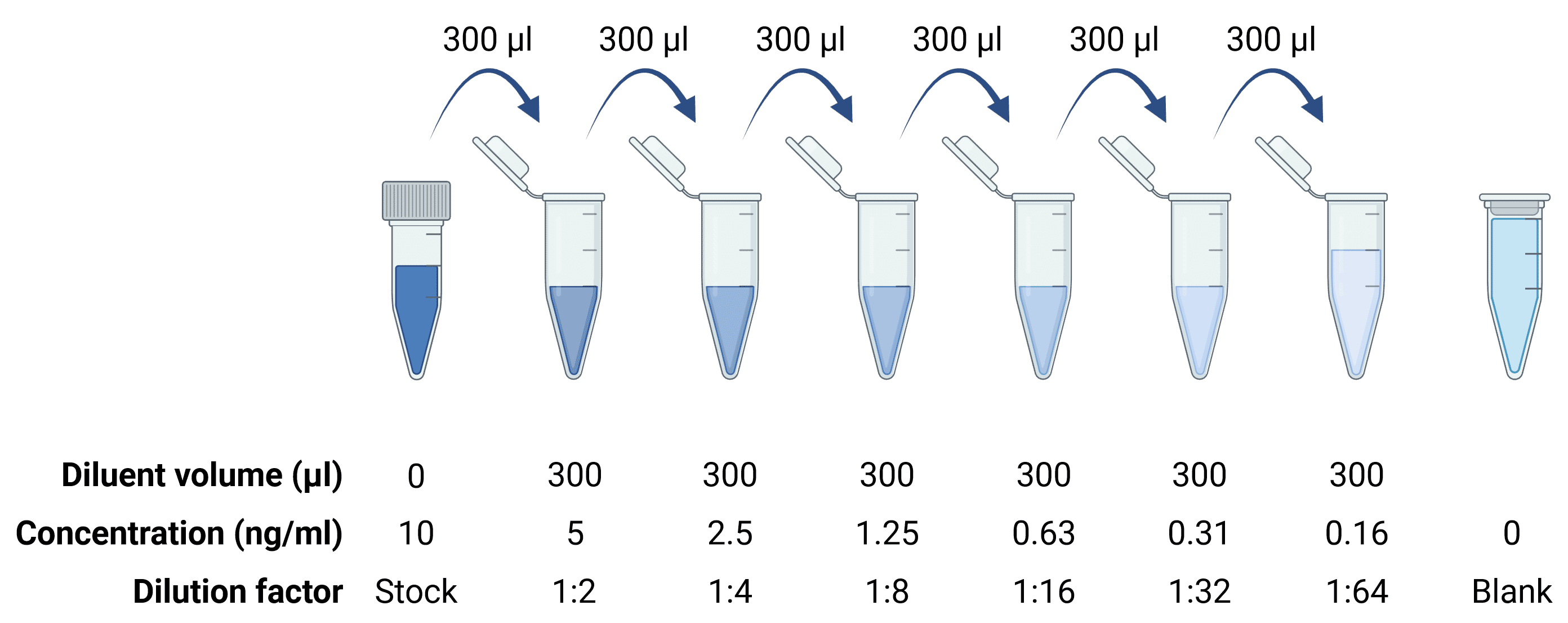
A standard stock solution typically represents a concentration of analyte of 1,000-10,000 pg/ml, which is then serially diluted 6 or 7 times to create the standards needed for the standard curve. For higher sensitivity ELISAs that are capable of detecting antigen to sub-picogram levels, a standard curve will start at a lower stock concentration, but the procedure will be the same, performing serial 1:2 or 1:3 dilutions.
Figure 4: Serial dilutions to generate a standard curve.
All ELISA kits sold by Antibodies.com come with a pre-prepared TMB Substrate solution. To make it from scratch, see the recipes below.
TMB substrate solution
TMB stock solution
Phosphate-citrate buffer, 0.5 M
TMB working chromogen solution
pNPP substrate solution
0.1M Glycine buffer
Dissolve pNPP in 0.1 M glycine buffer to a concentration of 1 mg/ml.
HRP stop solution
AP stop solution