General Notes
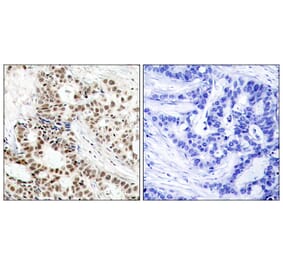
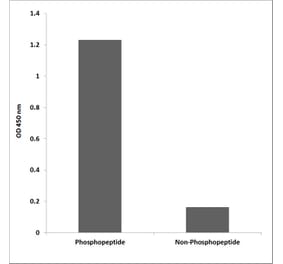
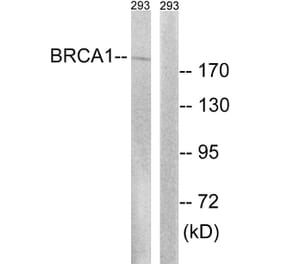
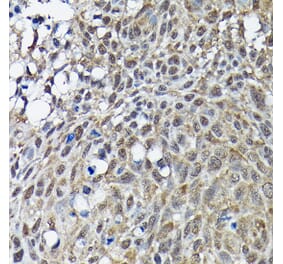
Mouse anti Human BRCA1 antibody, clone BR64 recognizes an epitope within the100 amino acid N-Terminal (NT) regionof human BRCA1, otherwise known as breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein, a tumor suppressor gene and major player in DNA damage repair, predominantly expressed in the nucleus during the S/G2 phase of the cell cycle.Along with BRCA2, BRCA1 is a high risk gene which is associated with hereditary breast and ovarian cancers, particularly at a younger age of diagnosis. Women carrying the BRCA1 mutation have a 50-95% chance of developing breast cancer in later life, but genetic screening and increased awareness of preventative surgery can reduce this risk significantly (Ford et al. 1994). Deleterious BRCA1 mutations may also increase the risk of other cancers in both males and females including pancreatic cancer, although in males pancreatic and prostate cancer appear to be more strongly associated with BRCA2 gene mutations.BRCA1 is a key marker of triple-negative breast cancer/TNBC (ER-/PR-/HER2-), a high risk aggressive cancer which makes up about 15% of invasive breast cancers, and which lacks the benefit of specific therapy that targets the three major proteins ER/PR/HER2. Triple-negative tumors are predominantly basal-like, poorly differentiated and of higher histological grade. Younger women have an increased rate of basal or BRCA related TNBC, compared with the higher proportion of apocrine, normal-like and rare subtypes of TNBC, seen in older women.During the characterization of clone BR64, it was determined that this antibody can be used in the identification of both native and denatured BRCA1, recognizing an epitope within amino acids 80-100 (Maul, G.G. et al. ).Mouse anti Human BRCA1 antibody, clone BR64 is suitable for use in immunofluorescence, showing both a nuclear distribution and reaction with the centrosome.




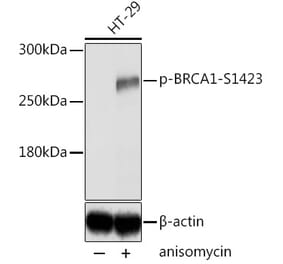
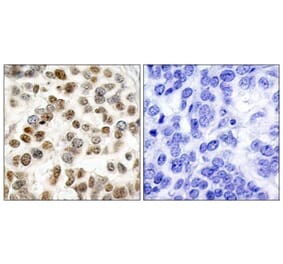
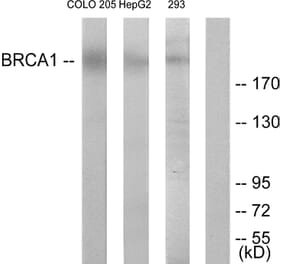
![Immunohistochemistry - Anti-BRCA1 Antibody [BRCA1/1398] (A250054) - Antibodies.com](https://cdn.antibodies.com/image/catalog/250/A250054_1.jpg?profile=product_alternative)