Unconjugated
Human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-G plays a crucial role in conferring fetal-maternal tolerance and ensuring a successful pregnancy. CD56bright natural killer (NK) cells accumulate at the maternal decidua in large numbers during pregnancy and are found in direct contact with fetal trophoblasts. There are increasing evidences that decidual NK (dNK) cells are crucial for pregnancy. However, the regulation of dNK cells is mostly unknown. Here, we provide evidences that the secretion function of dNK cells in recurrent spontaneous abortion was impaired, which led to the impairment of the proinvasion and proangiogenesis functions of dNK cells. Decreased HLA-G expression induced by the transfection of miR-133a mimics in HTR-8/SVneo affected the secretory functions of dNK cells. Thus, our data revealed that the functions of dNK cells could be suppressed by the decreased expression of HLA-G and suggest a possible mechanism of recurrent miscarriage.
RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) are key players in post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression in eukaryotic cells. To be able to unbiasedly identify RBPs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, we developed a yeast RNA interactome capture protocol which employs RNA labeling, covalent UV crosslinking of RNA and proteins at 365nm wavelength (photoactivatable-ribonucleoside-enhanced crosslinking, PAR-CL) and finally purification of the protein-bound mRNA. The method can be easily implemented in common workflows and takes about 3days to complete. Next to a comprehensive explanation of the method, we focus on our findings about the choice of crosslinking in yeast and discuss the rationale of individual steps in the protocol.
Upon infection, an activated CD4+ T cell produces terminally differentiated effector cells and renews itself for continued defense. In this study, we show that differentiation and self-renewal arise as opposing outcomes of sibling CD4+ T cells. After influenza challenge, antigen-specific cells underwent several divisions in draining lymph nodes (LN; DLNs) while maintaining expression of TCF1. After four or five divisions, some cells silenced, whereas some cells maintained TCF1 expression. TCF1-silenced cells were T helper 1-like effectors and concentrated in the lungs. Cells from earliest divisions were memory-like and concentrated in nondraining LN. TCF1-expressing cells from later divisions in the DLN could self-renew, clonally yielding a TCF1-silenced daughter cell as well as a sibling cell maintaining TCF1 expression. Some TCF1-expressing cells in DLNs acquired an alternative, follicular helper-like fate. Modeled differentiation experiments in vitro suggested that unequal PI3K/mechanistic target of rapamycin signaling drives intraclonal cell fate heterogeneity. Asymmetric division enables self-renewal to be coupled to production of differentiated CD4+ effector T cells during clonal selection.
The mechanism of action of valproate (VPA), a widely prescribed short chain fatty acid with anticonvulsant and anticancer properties, remains poorly understood. Here, the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae was used as model to investigate the biological consequences of VPA exposure. We found that low pH strongly potentiates VPA-induced growth inhibition. Transcriptional profiling revealed that under these conditions, VPA modulates the expression of genes involved in diverse cellular processes including protein folding, cell wall organisation, sexual reproduction, and cell cycle progression. We further investigated the impact of VPA on selected processes and found that this drug: i) activates markers of the unfolded protein stress response such as Hac1 mRNA splicing; ii) modulates the cell wall integrity pathway by inhibiting the activation of the Slt2 MAP kinase, and synergizes with cell wall stressors such as micafungin and calcofluor white in preventing yeast growth; iii) prevents activation of the Kss1 and Fus3 MAP kinases of the mating pheromone pathway, which in turn abolishes cellular responses to alpha factor; and iv) blocks cell cycle progression and DNA replication. Overall, our data identify heretofore unknown biological responses to VPA in budding yeast, and highlight the broad spectrum of cellular pathways influenced by this chemical in eukaryotes.
Neurons have a central role in the systemic coordination of mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt) and the cell non-autonomous modulation of longevity. However, the mechanism by which the nervous system senses mitochondrial stress and communicates to the distal tissues to induce UPRmt remains unclear. Here we employ the tissue-specific CRISPR-Cas9 approach to disrupt mitochondrial function only in the nervous system of Caenorhabditis elegans, and reveal a cell non-autonomous induction of UPRmt in peripheral cells. We further show that a neural sub-circuit composed of three types of sensory neurons, and one interneuron is required for sensing and transducing neuronal mitochondrial stress. In addition, neuropeptide FLP-2 functions in this neural sub-circuit to signal the non-autonomous UPRmt. Taken together, our results suggest a neuropeptide coordination of mitochondrial stress response in the nervous system.
Arginyltransferase 1 (Ate1) mediates protein arginylation, a poorly understood protein posttranslational modification (PTM) in eukaryotic cells. Previous evidence suggest a potential involvement of arginylation in stress response and this PTM was traditionally considered anti-apoptotic based on the studies of individual substrates. However, here we found that arginylation promotes cell death and/or growth arrest, depending on the nature and intensity of the stressing factor. Specifically, in yeast, mouse and human cells, deletion or downregulation of the ATE1 gene disrupts typical stress responses by bypassing growth arrest and suppressing cell death events in the presence of disease-related stressing factors, including oxidative, heat, and osmotic stresses, as well as the exposure to heavy metals or radiation. Conversely, in wild-type cells responding to stress, there is an increase of cellular Ate1 protein level and arginylation activity. Furthermore, the increase of Ate1 protein directly promotes cell death in a manner dependent on its arginylation activity. Finally, we found Ate1 to be required to suppress mutation frequency in yeast and mammalian cells during DNA-damaging conditions such as ultraviolet irradiation. Our study clarifies the role of Ate1/arginylation in stress response and provides a new mechanism to explain the link between Ate1 and a variety of diseases including cancer. This is also the first example that the modulation of the global level of a PTM is capable of affecting DNA mutagenesis.
The centromere, on which kinetochore proteins assemble, ensures precise chromosome segregation. Centromeres are largely specified by the histone H3 variant CENP-A (also known as Cse4 in yeasts). Structurally, centromere DNA sequences are highly diverse in nature. However, the evolutionary consequence of these structural diversities on de novo CENP-A chromatin formation remains elusive. Here, we report the identification of centromeres, as the binding sites of four evolutionarily conserved kinetochore proteins, in the human pathogenic budding yeast Candida tropicalis. Each of the seven centromeres comprises a 2 to 5 kb non-repetitive mid core flanked by 2 to 5 kb inverted repeats. The repeat-associated centromeres of C. tropicalis all share a high degree of sequence conservation with each other and are strikingly diverged from the unique and mostly non-repetitive centromeres of related Candida species--Candida albicans, Candida dubliniensis, and Candida lusitaniae. Using a plasmid-based assay, we further demonstrate that pericentric inverted repeats and the underlying DNA sequence provide a structural determinant in CENP-A recruitment in C. tropicalis, as opposed to epigenetically regulated CENP-A loading at centromeres in C. albicans. Thus, the centromere structure and its influence on de novo CENP-A recruitment has been significantly rewired in closely related Candida species. Strikingly, the centromere structural properties along with role of pericentric repeats in de novo CENP-A loading in C. tropicalis are more reminiscent to those of the distantly related fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Taken together, we demonstrate, for the first time, fission yeast-like repeat-associated centromeres in an ascomycetous budding yeast.
In sexually reproducing organisms, accurate gametogenesis is crucial for the transmission of genetic material from one generation to the next. This requires the faithful segregation of chromosomes during mitotic and meiotic divisions. One of the main players in this process is the kinetochore, a large multi-protein complex that forms at the interface of centromeres and microtubules. Here, we analyzed the expression profile and function of small kinetochore-associated protein (SKAP) in the mouse. We found that two distinct SKAP isoforms are specifically expressed in the germline: a smaller isoform, which is detected in spermatogonia and spermatocytes and localized in the outer mitotic and meiotic kinetochores from metaphase to telophase, and a larger isoform, which is expressed in the cytoplasm of elongating spermatids. We generated SKAP-deficient mice and found that testis size and sperm production were severely reduced in mutant males. This phenotype was partially caused by defects during spermatogonia proliferation before entry into meiosis. We conclude that mouse SKAP, while being dispensable for somatic cell divisions, has an important role in the successful outcome of male gametogenesis. In germ cells, analogous to what has been suggested in studies using immortalized cells, SKAP most likely stabilizes the interaction between kinetochores and microtubules, where it might be needed as an extra safeguard to ensure the correct segregation of mitotic and meiotic chromosomes.
© 2016 The authors.
RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) exert a broad range of biological functions. To explore the scope of RBPs across eukaryotic evolution, we determined the in vivo RBP repertoire of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae and identified 678 RBPs from yeast and additionally 729 RBPs from human hepatocytic HuH-7 cells. Combined analyses of these and recently published data sets define the core RBP repertoire conserved from yeast to man. Conserved RBPs harbour defined repetitive motifs within disordered regions, which display striking evolutionary expansion. Only 60% of yeast and 73% of the human RBPs have functions assigned to RNA biology or structural motifs known to convey RNA binding, and many intensively studied proteins surprisingly emerge as RBPs (termed 'enigmRBPs'), including almost all glycolytic enzymes, pointing to emerging connections between gene regulation and metabolism. Analyses of the mitochondrial hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (HSD17B10) uncover the RNA-binding specificity of an enigmRBP.
Nucleotide excision repair (NER) is a highly conserved pathway that removes helix-distorting DNA lesions induced by a plethora of mutagens, including UV light. Our laboratory previously demonstrated that human cells deficient in either ATM and Rad3-related (ATR) kinase or translesion DNA polymerase ? (i.e. key proteins that promote the completion of DNA replication in response to UV-induced replicative stress) are characterized by profound inhibition of NER exclusively during S phase. Toward elucidating the mechanistic basis of this phenomenon, we developed a novel assay to quantify NER kinetics as a function of cell cycle in the model organism Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Using this assay, we demonstrate that in yeast, deficiency of the ATR homologue Mec1 or of any among several other proteins involved in the cellular response to replicative stress significantly abrogates NER uniquely during S phase. Moreover, initiation of DNA replication is required for manifestation of this defect, and S phase NER proficiency is correlated with the capacity of individual mutants to respond to replicative stress. Importantly, we demonstrate that partial depletion of Rfa1 recapitulates defective S phase-specific NER in wild type yeast; moreover, ectopic RPA1-3 overexpression rescues such deficiency in either ATR- or polymerase ?-deficient human cells. Our results strongly suggest that reduction of NER capacity during periods of enhanced replicative stress, ostensibly caused by inordinate sequestration of RPA at stalled DNA replication forks, represents a conserved feature of the multifaceted eukaryotic DNA damage response.
Autophagy is a conserved homeostatic process active in all human cells and affecting a spectrum of diseases. Here we use a pharmaceutical screen to discover new mechanisms for activation of autophagy. We identify a subset of pharmaceuticals inducing autophagic flux with effects in diverse cellular systems modelling specific stages of several human diseases such as HIV transmission and hyperphosphorylated tau accumulation in Alzheimer's disease. One drug, flubendazole, is a potent inducer of autophagy initiation and flux by affecting acetylated and dynamic microtubules in a reciprocal way. Disruption of dynamic microtubules by flubendazole results in mTOR deactivation and dissociation from lysosomes leading to TFEB (transcription factor EB) nuclear translocation and activation of autophagy. By inducing microtubule acetylation, flubendazole activates JNK1 leading to Bcl-2 phosphorylation, causing release of Beclin1 from Bcl-2-Beclin1 complexes for autophagy induction, thus uncovering a new approach to inducing autophagic flux that may be applicable in disease treatment.
Cell size fundamentally affects all biosynthetic processes by determining the scale of organelles and influencing surface transport. Although extensive studies have identified many mutations affecting cell size, the molecular mechanisms underlying size control have remained elusive. In the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, size control occurs in G1 phase before Start, the point of irreversible commitment to cell division. It was previously thought that activity of the G1 cyclin Cln3 increased with cell size to trigger Start by initiating the inhibition of the transcriptional inhibitor Whi5 (refs 6-8). Here we show that although Cln3 concentration does modulate the rate at which cells pass Start, its synthesis increases in proportion to cell size so that its total concentration is nearly constant during pre-Start G1. Rather than increasing Cln3 activity, we identify decreasing Whi5 activity--due to the dilution of Whi5 by cell growth--as a molecular mechanism through which cell size controls proliferation. Whi5 is synthesized in S/G2/M phases of the cell cycle in a largely size-independent manner. This results in smaller daughter cells being born with higher Whi5 concentrations that extend their pre-Start G1 phase. Thus, at its most fundamental level, size control in budding yeast results from the differential scaling of Cln3 and Whi5 synthesis rates with cell size. More generally, our work shows that differential size-dependency of protein synthesis can provide an elegant mechanism to coordinate cellular functions with growth.
Fungal infections are a leading cause of morbidity and death for hospitalized patients, mainly because they remain difficult to diagnose and to treat. Diseases range from widespread superficial infections such as vulvovaginal infections to life-threatening systemic candidiasis. For systemic mycoses, only a restricted arsenal of antifungal agents is available. Commonly used classes of antifungal compounds include azoles, polyenes, and echinocandins. Due to emerging resistance to standard therapies, significant side effects, and high costs for several antifungals, there is a need for new antifungals in the clinic. In order to expand the arsenal of compounds with antifungal activity, we previously screened a compound library using a cell-based screening assay. A set of novel benzimidazole derivatives, including (S)-2-(1-aminoisobutyl)-1-(3-chlorobenzyl)benzimidazole (EMC120B12), showed high antifungal activity against several species of pathogenic yeasts, including Candida glabrata and Candida krusei (species that are highly resistant to antifungals). In this study, comparative analysis of EMC120B12 versus fluconazole and nocodazole, using transcriptional profiling and sterol analysis, strongly suggested that EMC120B12 targets Erg11p in the ergosterol biosynthesis pathway and not microtubules, like other benzimidazoles. In addition to the marker sterol 14-methylergosta-8,24(28)-dien-3ß,6a-diol, indicating Erg11p inhibition, related sterols that were hitherto unknown accumulated in the cells during EMC120B12 treatment. The novel sterols have a 3ß,6a-diol structure. In addition to the identification of novel sterols, this is the first time that a benzimidazole structure has been shown to result in a block of the ergosterol pathway.
TOR and PKA signaling pathways control eukaryotic cell growth and proliferation. TOR activity in model fungi, such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae, responds principally to nutrients, e.g., nitrogen and phosphate sources, which are incorporated into the growing cell mass; PKA signaling responds to the availability of the cells' major energy source, glucose. In the fungal commensal and pathogen, Candida albicans, little is known of how these pathways interact. Here, the signal from phosphorylated ribosomal protein S6 (P-S6) was defined as a surrogate marker for TOR-dependent anabolic activity in C. albicans. Nutritional, pharmacologic and genetic modulation of TOR activity elicited corresponding changes in P-S6 levels. The P-S6 signal corresponded to translational activity of a GFP reporter protein. Contributions of four PKA pathway components to anabolic activation were then examined. In high glucose concentrations, only Tpk2 was required to upregulate P-S6 to physiologic levels, whereas all four tested components were required to downregulate P-S6 in low glucose. TOR was epistatic to PKA components with respect to P-S6. In many host niches inhabited by C. albicans, glucose is scarce, with protein being available as a nitrogen source. We speculate that PKA may modulate TOR-dependent cell growth to a rate sustainable by available energy sources, when monomers of anabolic processes, such as amino acids, are abundant.
Defects in the completion of cell division by cytokinesis have long been proposed to foster carcinogenesis by engendering chromosome instability, but few tumor suppressor mechanisms controlling this process have so far been identified. Here, we identify a carboxyl (C)-terminal region of the high-mobility group protein HMG20b that is essential for cytokinesis, and report that it is inactivated by a cancer-associated mutation. We find that a C-terminal region of HMG20b spanning residues 173-317 is necessary and sufficient not only for its localization to cytokinetic structures, but also for its interaction with the tumor suppressor BRCA2, implicated in the abscission step of cytokinesis. Indeed, expression of this C-terminal HMG20b region suffices to restore cytokinesis in HMG20b-depleted cells. The non-conservative substitution of HMG20b residue Ala247 with Pro, reported in human lung cancer, disrupts these activities of HMG20b, impairing cytokinesis in a trans-dominant manner. Our findings provide fresh insight into the mechanism by which the HMG20b-BRCA2 complex controls mitotic cell division, and implicate heterozygous HMG20b mutations affecting cytokinesis regulation in the genesis of human cancers.
Communication between cortical cell polarity cues and the mitotic spindle ensures proper orientation of cell divisions within complex tissues. Defects in mitotic spindle positioning have been linked to various developmental disorders and have recently emerged as a potential contributor to tumorigenesis. Despite the importance of this process to human health, the molecular mechanisms that regulate spindle orientation are not fully understood. Moreover, it remains unclear how diverse cortical polarity complexes might cooperate to influence spindle positioning. We and others have demonstrated spindle orientation roles for Dishevelled (Dsh), a key regulator of planar cell polarity, and Discs large (Dlg), a conserved apico-basal cell polarity regulator, effects which were previously thought to operate within distinct molecular pathways. Here we identify a novel direct interaction between the Dsh-PDZ domain and the alternatively spliced "I3-insert" of the Dlg-Hook domain, thus establishing a potential convergent Dsh/Dlg pathway. Furthermore, we identify a Dlg sequence motif necessary for the Dsh interaction that shares homology to the site of Dsh binding in the Frizzled receptor. Expression of Dsh enhanced Dlg-mediated spindle positioning similar to deletion of the Hook domain. This Dsh-mediated activation was dependent on the Dlg-binding partner, GukHolder (GukH). These results suggest that Dsh binding may regulate core interdomain conformational dynamics previously described for Dlg. Together, our results identify Dlg as an effector of Dsh signaling and demonstrate a Dsh-mediated mechanism for the activation of Dlg/GukH-dependent spindle positioning. Cooperation between these two evolutionarily-conserved cell polarity pathways could have important implications to both the development and maintenance of tissue homeostasis in animals.
MicroRNA (miRNA) is a small, non-coding RNAs and it could post-transcriptionally related gene expression by negatively regulating the stability or translational efficiency of their target genes. Previous studies have reported the antineoplastic effect of microRNA-29b (miR-29b) in several kinds of cancers. The aim of this study was to investigate the potential role of miR-29b in human osteosarcoma pathogenesis. Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was performed to determine the expression level of miR-29b in 20 osteosarcoma specimens and adjacent normal bone tissues. The proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion were employed to detect the effect of miR-29b on the osteosarcoma cell line MG63. The results showed that miR-29b expression was relatively decreased in osteosarcoma specimens compared with adjacent normal tissues. Overexpression of miR-29b suppressed MG63 cell proliferation, migration and invasion. Meanwhile miR-29b could induce apoptosis of MG63. Besides, miR-29b directly targets VEGF and over-expression of miR-29b led to down-regulation of VEGF protein level, In conclusions, miR-29b may play an important role in osteosarcoma progression, which might negatively regulate the expression of VEGF and suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis of MG63 cell line.
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Sro7 and Sro77 are homologues of the Drosophila tumour suppressor lethal giant larvae (Lgl), which regulates cell polarity in Drosophila epithelial cells. Here, we showed that double mutation of SRO7/SRO77 was defective in colony growth. The colony of the SRO7/SRO77 double deletion was much smaller than the WT and appeared to be round with a smooth surface, compared with the WT. Analysis using transmission electron microscopy revealed multiple defects of the colony cells, including multiple budding, multiple nuclei, cell lysis and dead cells, suggesting that the double deletion caused defects in cell polarity and cell wall integrity (CWI). Overexpression of RHO1, one of the central regulators of cell polarity and CWI, fully recovered the sro7?/sro77? phenotype. We further demonstrated that sro7?/sro77? caused a decrease of the GTP-bound, active Rho1, which in turn caused an upregulation of TOR1. Deletion of TOR1 in sro7?/sro77? (sro7?/sro77?/tor1?) recovered the cell growth and colony morphology, similar to WT. Our results suggested that the tumour suppressor homologue SRO7/SRO77 regulated cell proliferation and yeast colony development via the Rho1-Tor1 pathway.
In S. cerevisiae, replication timing is controlled by epigenetic mechanisms restricting the accessibility of origins to limiting initiation factors. About 30% of these origins are located within repetitive DNA sequences such as the ribosomal DNA (rDNA) array, but their regulation is poorly understood. Here, we have investigated how histone deacetylases (HDACs) control the replication program in budding yeast. This analysis revealed that two HDACs, Rpd3 and Sir2, control replication timing in an opposite manner. Whereas Rpd3 delays initiation at late origins, Sir2 is required for the timely activation of early origins. Moreover, Sir2 represses initiation at rDNA origins, whereas Rpd3 counteracts this effect. Remarkably, deletion of SIR2 restored normal replication in rpd3? cells by reactivating rDNA origins. Together, these data indicate that HDACs control the replication timing program in budding yeast by modulating the ability of repeated origins to compete with single-copy origins for limiting initiation factors.
Group II introns are commonly believed to be the progenitors of spliceosomal introns, but they are notably absent from nuclear genomes. Barriers to group II intron function in nuclear genomes therefore beg examination. A previous study showed that nuclear expression of a group II intron in yeast results in nonsense-mediated decay and translational repression of mRNA, and that these roadblocks to expression are group II intron-specific. To determine the molecular basis for repression of gene expression, we investigated cellular dynamics of processed group II intron RNAs, from transcription to cellular localization. Our data show pre-mRNA mislocalization to the cytoplasm, where the RNAs are targeted to foci. Furthermore, tenacious mRNA-pre-mRNA interactions, based on intron-exon binding sequences, result in reduced abundance of spliced mRNAs. Nuclear retention of pre-mRNA prevents this interaction and relieves these expression blocks. In addition to providing a mechanistic rationale for group II intron-specific repression, our data support the hypothesis that RNA silencing of the host gene contributed to expulsion of group II introns from nuclear genomes and drove the evolution of spliceosomal introns.
In closed mitotic systems such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae, nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) and the spindle pole body (SPB) must assemble into an intact nuclear envelope (NE). Ndc1 is a highly conserved integral membrane protein involved in insertion of both complexes. In this study, we show that Ndc1 interacts with the SUN domain-containing protein Mps3 on the NE in live yeast cells using fluorescence cross-correlation spectroscopy. Genetic and molecular analysis of a series of new ndc1 alleles allowed us to understand the role of Ndc1-Mps3 binding at the NE. We show that the ndc1-L562S allele is unable to associate specifically with Mps3 and find that this mutant is lethal due to a defect in SPB duplication. Unlike other ndc1 alleles, the growth and Mps3 binding defect of ndc1-L562S is fully suppressed by deletion of POM152, which encodes a NPC component. Based on our data we propose that the Ndc1-Mps3 interaction is important for controlling the distribution of Ndc1 between the NPC and SPB.
Dendritic cells sample the environment for antigens and play an important role in establishing the link between innate and acquired immunity. Dendritic cells contain mechanosensitive adhesive structures called podosomes that consist of an actin-rich core surrounded by integrins, adaptor proteins and actin network filaments. They facilitate cell migration via localized degradation of extracellular matrix. Here, we show that podosomes of human dendritic cells locate to spots of low physical resistance in the substrate (soft spots) where they can evolve into protrusive structures. Pathogen recognition receptors locate to these protrusive structures where they can trigger localized antigen uptake, processing and presentation to activate T-cells. Our data demonstrate a novel role in antigen sampling for the podosomes of dendritic cells.
DNA replication in all organisms requires polymerases to synthesize copies of the genome. DNA polymerases are unable to function on a bare template and require a primer. Primases are crucial RNA polymerases that perform the initial de novo synthesis, generating the first 8-10 nucleotides of the primer. Although structures of archaeal and bacterial primases have provided insights into general priming mechanisms, these proteins are not well conserved with heterodimeric (p48/p58) primases in eukaryotes. Here, we present X-ray crystal structures of the catalytic engine of a eukaryotic primase, which is contained in the p48 subunit. The structures of p48 reveal that eukaryotic primases maintain the conserved catalytic prim fold domain, but with a unique subdomain not found in the archaeal and bacterial primases. Calorimetry experiments reveal that Mn(2+) but not Mg(2+) significantly enhances the binding of nucleotide to primase, which correlates with higher catalytic efficiency in vitro. The structure of p48 with bound UTP and Mn(2+) provides insights into the mechanism of nucleotide synthesis by primase. Substitution of conserved residues involved in either metal or nucleotide binding alter nucleotide binding affinities, and yeast strains containing the corresponding Pri1p substitutions are not viable. Our results reveal that two residues (S160 and H166) in direct contact with the nucleotide were previously unrecognized as critical to the human primase active site. Comparing p48 structures to those of similar polymerases in different states of action suggests changes that would be required to attain a catalytically competent conformation capable of initiating dinucleotide synthesis.
Mutations in the dysferlin gene resulting in dysferlin-deficiency lead to limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 2B and Myoshi myopathy in humans. Dysferlin has been proposed as a critical regulator of vesicle-mediated membrane resealing in muscle fibers, and localizes to muscle fiber wounds following sarcolemma damage. Studies in fibroblasts and urchin eggs suggest that trafficking and fusion of intracellular vesicles with the plasma membrane during resealing requires the intracellular cytoskeleton. However, the contribution of dysferlin-containing vesicles to resealing in muscle and the role of the cytoskeleton in regulating dysferlin-containing vesicle biology is unclear. Here, we use live-cell imaging to examine the behavior of dysferlin-containing vesicles following cellular wounding in muscle cells and examine the role of microtubules and kinesin in dysferlin-containing vesicle behavior following wounding. Our data indicate that dysferlin-containing vesicles move along microtubules via the kinesin motor KIF5B in muscle cells. Membrane wounding induces dysferlin-containing vesicle-vesicle fusion and the formation of extremely large cytoplasmic vesicles, and this response depends on both microtubules and functional KIF5B. In non-muscle cell types, lysosomes are critical mediators of membrane resealing, and our data indicate that dysferlin-containing vesicles are capable of fusing with lysosomes following wounding which may contribute to formation of large wound sealing vesicles in muscle cells. Overall, our data provide mechanistic evidence that microtubule-based transport of dysferlin-containing vesicles may be critical for resealing, and highlight a critical role for dysferlin-containing vesicle-vesicle and vesicle-organelle fusion in response to wounding in muscle cells.
Aberrant expression of microRNAs (miRNAs), a class of small non-coding regulatory RNAs, has been implicated in the development and progression of high-grade gliomas. However, the precise mechanistic role of many miRNAs in this disease remains unclear. Here, we investigate the functional role of miR-331-3p in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). We found that miR-331-3p expression in GBM cell lines is significantly lower than in normal brain, and that transient overexpression of miR-331-3p inhibits GBM cell line proliferation and clonogenic growth, suggesting a possible tumor suppressor role for miR-331-3p in this system. Bioinformatics analysis identified neuropilin-2 (NRP-2) as a putative target of miR-331-3p. Using transfection studies, we validated NRP-2 mRNA as a target of miR-331-3p in GBM cell lines, and show that NRP-2 expression is regulated by miR-331-3p. RNA interference (RNAi) to inhibit NRP-2 expression in vitro decreased the growth and clonogenic growth of GBM cell lines, providing further support for an oncogenic role for NRP-2 in high-grade gliomas. We also show that miR-331-3p inhibits GBM cell migration, an effect due in part to reduced NRP-2 expression. Finally, we identified a significant inverse correlation between miR-331-3p and NRP-2 expression in The Cancer Genome Atlas GBM cohort of 491 patients. Together, our results suggest that a loss of miR-331-3p expression contributes to GBM development and progression, at least in part via upregulating NRP-2 expression and increasing cell proliferation and clonogenic growth.
Multinucleate cells play an important role in higher plants, especially during reproduction; however, the configurations of their cytoskeletons, which are formed as a result of mitosis without cytokinesis, have mainly been studied in coenocytes. Previous authors have proposed that in spite of their developmental origin (cell fusion or mitosis without cytokinesis), in multinucleate plant cells, radiating microtubules determine the regular spacing of individual nuclei. However, with the exception of specific syncytia induced by parasitic nematodes, there is no information about the microtubular cytoskeleton in plant heterokaryotic syncytia, i.e. when the nuclei of fused cells come from different cell pools. In this paper, we describe the arrangement of microtubules in the endosperm and special endosperm-placenta syncytia in two Utricularia species. These syncytia arise from different progenitor cells, i.e. cells of the maternal sporophytic nutritive tissue and the micropylar endosperm haustorium (both maternal and paternal genetic material). The development of the endosperm in the two species studied was very similar. We describe microtubule configurations in the three functional endosperm domains: the micropylar syncytium, the endosperm proper and the chalazal haustorium. In contrast to plant syncytia that are induced by parasitic nematodes, the syncytia of Utricularia had an extensive microtubular network. Within each syncytium, two giant nuclei, coming from endosperm cells, were surrounded by a three-dimensional cage of microtubules, which formed a huge cytoplasmic domain. At the periphery of the syncytium, where new protoplasts of the nutritive cells join the syncytium, the microtubules formed a network which surrounded small nuclei from nutritive tissue cells and were also distributed through the cytoplasm. Thus, in the Utricularia syncytium, there were different sized cytoplasmic domains, whose architecture depended on the source and size of the nuclei. The endosperm proper was isolated from maternal (ovule) tissues by a cuticle layer, so the syncytium and chalazal haustorium were the only way for nutrients to be transported from the maternal tissue towards the developing embryo.
Gametes are among the most highly specialized cells produced during development. Although gametogenesis culminates in transcriptional quiescence in plants and animals, regulatory mechanisms controlling this are unknown. Here, we confirm that gamete differentiation in the single-celled yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is accompanied by global transcriptional shutoff following the completion of meiosis. We show that Jhd2, a highly conserved JARID1-family histone H3K4 demethylase, activates protein-coding gene transcription in opposition to this programmed transcriptional shutoff, sustaining the period of productive transcription during spore differentiation. Moreover, using genome-wide nucleosome, H3K4me, and transcript mapping experiments, we demonstrate that JHD2 globally represses intergenic noncoding transcription during this period. The widespread transcriptional defects of JHD2 mutants are associated with precocious differentiation and the production of stress-sensitive spores, demonstrating that Jhd2 regulation of the global postmeiotic transcriptional program is critical for the production of healthy meiotic progeny.
We have previously identified a Rho protein, RhoD, which localizes to the plasma membrane and the early endocytic compartment. Here, we show that a GTPase-deficient mutant of RhoD, RhoDG26V, causes hyperplasia and perturbed differentiation of the epidermis, when targeted to the skin of transgenic mice. In vitro, gain-of-function and loss-of-function approaches revealed that RhoD is involved in the regulation of G1/S-phase progression and causes overduplication of centrosomes. Centriole overduplication assays in aphidicolin-arrested p53-deficient U2OS cells, in which the cell and the centrosome cycles are uncoupled, revealed that the effects of RhoD and its mutants on centrosome duplication and cell cycle are independent. Enhancement of G1/S-phase progression was mediated via Diaph1, a novel effector of RhoD, which we have identified using a two-hybrid screen. These results indicate that RhoD participates in the regulation of cell-cycle progression and centrosome duplication.
Intracellular deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate (dNTP) pools must be tightly regulated to preserve genome integrity. Indeed, alterations in dNTP pools are associated with increased mutagenesis, genomic instability and tumourigenesis. However, the mechanisms by which altered or imbalanced dNTP pools affect DNA synthesis remain poorly understood. Here, we show that changes in intracellular dNTP levels affect replication dynamics in budding yeast in different ways. Upregulation of the activity of ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) increases elongation, indicating that dNTP pools are limiting for normal DNA replication. In contrast, inhibition of RNR activity with hydroxyurea (HU) induces a sharp transition to a slow-replication mode within minutes after S-phase entry. Upregulation of RNR activity delays this transition and modulates both fork speed and origin usage under replication stress. Interestingly, we also observed that chromosomal instability (CIN) mutants have increased dNTP pools and show enhanced DNA synthesis in the presence of HU. Since upregulation of RNR promotes fork progression in the presence of DNA lesions, we propose that CIN mutants adapt to chronic replication stress by upregulating dNTP pools.
ERBB-2 overexpression is associated with the development and progression of cancer and mediates its resistance to therapy. It has been suggested that post-transcriptional mechanisms control the overexpression of ERBB-2 in prostate cancer (PCa). We recently demonstrated that the 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) of ERBB-2 mRNA contains two specific target sites for binding of the microRNA miR-331-3p and that miR-331-3p represses ERBB-2 expression and signaling in PCa cells. Here we investigate a U-rich element situated in close proximity to the distal miR-331-3p target site in the ERBB-2 3'-UTR. Specific binding of HuR to this U-rich element promotes ERBB-2 expression in PCa cells. We show that HuR antagonizes the repressive action of miR-331-3p on its distal ERBB-2 3'-UTR target site. These results support a model in which the interplay between RNA-binding proteins and microRNAs controls the post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression and suggest that both HuR and miR-331-3p participate in the overexpression of ERBB-2 observed in some PCas.
The striated muscle-specific tripartite motif (TRIM) proteins TRIM63/MURF1, TRIM55/MURF2 and TRIM54/MURF3 can function as ubiquitin E3 ligases in ubiquitin-mediated muscle protein turnover. Despite their well-characterised roles in muscle atrophy, the dynamics of MURF expression in the development and early postnatal adaptation of striated muscle is largely unknown. Here, we show that MURF2 is expressed at the very onset of mouse cardiac differentiation at embryonic day 8.5, and represents a sensitive marker for differentiating myocardium. During cardiac development, expression shifts from the 50 kDa to the 60 kDa A-isoform, which dominates postnatally. In contrast, MURF1 shows strong postnatal upregulation and MURF3 is not significantly expressed before birth. MURF2 expression parallels that of the autophagy-associated proteins LC3, p62/SQSTM1 and nbr1. SiRNA knockdown of MURF2 in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes disrupts posttranslational microtubule modification and myofibril assembly, and is only partly compensated by upregulation of MURF3 but not MURF1. Knockdown of both MURF2 and MURF3 severely disrupts the formation of ordered Z- and M-bands, likely by perturbed tubulin dynamics. These results suggest that ubiquitin-mediated protein turnover and MURF2 in particular play an unrecognised role in the earliest steps of heart muscle differentiation, and that partial complementation of MURF2 deficiency is afforded by MURF3.
Human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV) is a major cause of pediatric lower respiratory tract disease to which there is no vaccine or efficacious chemotherapeutic strategy. Although RNA synthesis and virus assembly occur in the cytoplasm, HRSV is known to induce nuclear responses in the host cell as replication alters global gene expression. Quantitative proteomics was used to take an unbiased overview of the protein changes in transformed human alveolar basal epithelial cells infected with HRSV. Underpinning this was the use of stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture coupled to LC-MS/MS, which allowed the direct and simultaneous identification and quantification of both cellular and viral proteins. To reduce sample complexity and increase data return on potential protein localization, cells were fractionated into nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts. This resulted in the identification of 1,140 cellular proteins and six viral proteins. The proteomics data were analyzed using Ingenuity Pathways Analysis to identify defined canonical pathways and functional groupings. Selected data were validated using Western blot, direct and indirect immunofluorescence confocal microscopy, and functional assays. The study served to validate and expand upon known HRSV-host cell interactions, including those associated with the antiviral response and alterations in subnuclear structures such as the nucleolus and ND10 (promyelocytic leukemia bodies). In addition, novel changes were observed in mitochondrial proteins and functions, cell cycle regulatory molecules, nuclear pore complex proteins and nucleocytoplasmic trafficking proteins. These data shed light into how the cell is potentially altered to create conditions more favorable for infection. Additionally, the study highlights the application and advantage of stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture coupled to LC-MS/MS for the analysis of virus-host interactions.
Asymmetric cell division is a potential means by which cell fate choices during an immune response are orchestrated. Defining the molecular mechanisms that underlie asymmetric division of T cells is paramount for determining the role of this process in the generation of effector and memory T cell subsets. In other cell types, asymmetric cell division is regulated by conserved polarity protein complexes that control the localization of cell fate determinants and spindle orientation during division. We have developed a tractable, in vitro model of naive CD8(+) T cells undergoing initial division while attached to dendritic cells during Ag presentation to investigate whether similar mechanisms might regulate asymmetric division of T cells. Using this system, we show that direct interactions with APCs provide the cue for polarization of T cells. Interestingly, the immunological synapse disseminates before division even though the T cells retain contact with the APC. The cue from the APC is translated into polarization of cell fate determinants via the polarity network of the Par3 and Scribble complexes, and orientation of the mitotic spindle during division is orchestrated by the partner of inscuteable/G protein complex. These findings suggest that T cells have selectively adapted a number of evolutionarily conserved mechanisms to generate diversity through asymmetric cell division.
Kaiso is a BTB/POZ zinc finger protein known as a transcriptional repressor. It was originally identified through its in vitro association with the Armadillo protein p120ctn. Subcellular localization of Kaiso in cell lines and in normal and cancerous human tissues revealed that its expression is not restricted to the nucleus. In the present study we monitored Kaiso's subcellular localization during the cell cycle and found the following: (1) during interphase, Kaiso is located not only in the nucleus, but also on microtubular structures, including the centrosome; (2) at metaphase, it is present at the centrosomes and on the spindle microtubules; (3) during telophase, it accumulates at the midbody. We found that Kaiso is a genuine PCM component that belongs to a pericentrin molecular complex. We analyzed the functions of different domains of Kaiso by visualizing the subcellular distribution of GFP-tagged Kaiso fragments throughout the cell cycle. Our results indicate that two domains are responsible for targeting Kaiso to the centrosomes and microtubules. The first domain, designated SA1 for spindle-associated domain 1, is located in the center of the Kaiso protein and localizes at the spindle microtubules and centrosomes; the second domain, SA2, is an evolutionarily conserved domain situated just before the zinc finger domain and might be responsible for localizing Kaiso towards the centrosomal region. Constructs containing both SA domains and Kaiso's aminoterminal BTB/POZ domain triggered the formation of abnormal centrosomes. We also observed that overexpression of longer or full-length Kaiso constructs led to mitotic cell arrest and frequent cell death. Knockdown of Kaiso accelerated cell proliferation. Our data reveal a new target for Kaiso at the centrosomes and spindle microtubules during mitosis. They also strongly imply that Kaiso's function as a transcriptional regulator might be linked to the control of the cell cycle and to cell proliferation in cancer.
Clathrin is involved in vesicle formation in the trans-Golgi network (TGN)/endosomal system and during endocytosis. Clathrin recruitment to membranes is mediated by the clathrin heavy chain (HC) N-terminal domain (TD), which forms a seven-bladed beta-propeller. TD binds membrane-associated adaptors, which have short peptide motifs, either the clathrin-box (CBM) and/or the W-box; however, the importance of the TD binding sites for these motifs has not been tested in vivo. We investigated the importance of the TD in clathrin function by generating 1) mutations in the yeast HC gene (CHC1) to disrupt the binding sites for the CBM and W-box (chc1-box), and 2) four TD-specific temperature-sensitive alleles of CHC1. We found that TD is important for the retention of resident TGN enzymes and endocytosis of alpha-factor; however, the known adaptor binding sites are not necessary, because chc1-box caused little to no effect on trafficking pathways involving clathrin. The Chc1-box TD was able to interact with the endocytic adaptor Ent2 in a CBM-dependent manner, and HCs encoded by chc1-box formed clathrin-coated vesicles. These data suggest that additional or alternative binding sites exist on the TD propeller to help facilitate the recruitment of clathrin to sites of vesicle formation.
In most cancers, transformation begins in a single cell in an epithelial cell sheet. However, it is not known what happens at the interface between non-transformed (normal) and transformed cells once the initial transformation has occurred. Using Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) epithelial cells that express constitutively active, oncogenic Ras (Ras(V12)) in a tetracycline-inducible system, we investigated the cellular processes arising at the interface between normal and transformed cells. We show that two independent phenomena occur in a non-cell-autonomous manner: when surrounded by normal cells, Ras(V12) cells are either apically extruded from the monolayer, or form dynamic basal protrusions and invade the basal matrix. Neither apical extrusion nor basal protrusion formation is observed when Ras(V12) cells are surrounded by other Ras(V12) cells. We show that Cdc42 and ROCK (also known as Rho kinase) have vital roles in these processes. We also demonstrate that E-cadherin knockdown in normal cells surrounding Ras(V12) cells reduces the frequency of apical extrusion, while promoting basal protrusion formation and invasion. These results indicate that Ras(V12)-transformed cells are able to recognize differences between normal and transformed cells, and consequently leave epithelial sheets either apically or basally, in a cell-context-dependent manner.
A crucial early event by which cancer cells switch from localised to invasive phenotype is initiated by the acquisition of autonomous motile properties; a process driven by dynamic assembly and disassembly of multiple focal adhesion (FA) proteins, which mediate cell-matrix attachments, extracellular matrix degradation, and serve as traction sites for cell motility. We have reported previously that cancer cell invasion induced by overexpression of members of the ErbB tyrosine kinase receptors, including ErbB2, is dependent on FA signalling through FA kinase (FAK). Here, we show that ErbB2 receptor signalling regulates FA turnover, and cell migration and invasion through the Src-FAK pathway. Inhibition of the Src-FAK signalling in ErbB2-positive cells by Herceptin or RNA interference selectively regulates FA turnover, leading to enhanced number and size of peripherally localised adhesions and inhibition of cell invasion. Inhibition of ErbB2 signalling failed to regulate FA and cell migration and invasion in cells lacking FAK or Src but gains this activity after restoration of these proteins. Taken together, our results show a regulation of FA turnover by ErbB2 signalling.
The Cse4p-containing centromere regions of Candida albicans have unique and different DNA sequences on each of the eight chromosomes. In a closely related yeast, C. dubliniensis, we have identified the centromeric histone, CdCse4p, and shown that it is localized at the kinetochore. We have identified putative centromeric regions, orthologous to the C. albicans centromeres, in each of the eight C. dubliniensis chromosomes by bioinformatic analysis. Chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by PCR using a specific set of primers confirmed that these regions bind CdCse4p in vivo. As in C. albicans, the CdCse4p-associated core centromeric regions are 3-5 kb in length and show no sequence similarity to one another. Comparative sequence analysis suggests that the Cse4p-rich centromere DNA sequences in these two species have diverged faster than other orthologous intergenic regions and even faster than our best estimated "neutral" mutation rate. However, the location of the centromere and the relative position of Cse4p-rich centromeric chromatin in the orthologous regions with respect to adjacent ORFs are conserved in both species, suggesting that centromere identity is not solely determined by DNA sequence. Unlike known point and regional centromeres of other organisms, centromeres in C. albicans and C. dubliniensis have no common centromere-specific sequence motifs or repeats except some of the chromosome-specific pericentric repeats that are found to be similar in these two species. We propose that centromeres of these two Candida species are of an intermediate type between point and regional centromeres.
Mitochondrial ribosomal RNAs (mtrRNAs) have been reported to translocate extra-mitochondrially and localize to the germ cell determinant of oocytes and zygotes in some metazoa except mammals. To address whether the mtrRNAs also localize in the mammals, expression and distribution of mitochondrion-encoded RNAs in the mouse oocytes and zygotes was examined by whole-mount in situ hybridization (ISH). Both 12S and 16S rRNAs were predominantly distributed in the animal hemisphere of the mature oocyte. This distribution pattern was rearranged toward the second polar body in zygotes after fertilization. The amount of mtrRNAs decreased around first cleavage, remained low during second cleavage and increased after third cleavage. Staining intensity of the 12S rRNA was weaker than that of the 16S rRNA throughout the examined stages. Similar distribution dynamics of the 16S rRNA was observed in strontium-activated haploid parthenotes, suggesting the distribution rearrangement does not require a component from sperm. The distribution of 16S rRNAs did not coincide with that of mitochondrion-specific heat shock protein 70, suggesting that the mtrRNA is translocated from mitochondria. The ISH-scanning electron microscopy confirms the extra-mitochondrial mtrRNA in the mouse oocyte. Chloramphenicol (CP) treatment of late pronuclear stage zygotes perturbed first cleavage as judged by the greater than normal disparity in size of blastomeres of 2-cell conceptuses. Two-third of the CP-treated zygotes arrested at either 2-cell or 3-cell stage even after the CP was washed out. These findings indicate that the extra-mitochondrial mtrRNAs are localized in the mouse oocyte and implicated in correct cytoplasmic segregation into blastomeres through cleavages of the zygote.
The signaling lipid, phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate (PI(3,5)P(2)), likely functions in multiple signaling pathways. Here, we report the characterization of a mouse mutant lacking Vac14, a regulator of PI(3,5)P(2) synthesis. The mutant mice exhibit massive neurodegeneration, particularly in the midbrain and in peripheral sensory neurons. Cell bodies of affected neurons are vacuolated, and apparently empty spaces are present in areas where neurons should be present. Similar vacuoles are found in cultured neurons and fibroblasts. Selective membrane trafficking pathways, especially endosome-to-TGN retrograde trafficking, are defective. This report, along with a recent report on a mouse with a null mutation in Fig4, presents the unexpected finding that the housekeeping lipid, PI(3,5)P(2), is critical for the survival of neural cells.
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) terminates neurotransmission at cholinergic synapses by hydrolysing acetylcholine, but also has non-enzymatic morphoregulatory effects on neurons such as stimulation of neurite outgrowth. It is widely expressed outside the nervous system, but its function in non-neuronal cells is unclear. Here we have investigated the distribution and function of AChE in fibroblasts and astrocytes. We show that these cells express high levels of AChE protein that co-migrates with recombinant AChE but contains little catalytic activity. Fibroblasts express transcripts encoding the synaptic AChE-T isoform and its membrane anchoring peptide PRiMA-I. AChE is strikingly distributed in arcs, rings and patches at the leading edge of spreading and migrating fibroblasts and astrocytes, close to the cell-substratum interface, and in neuronal growth cones. During in vivo healing of mouse skin, AChE becomes highly expressed in re-epithelialising epidermal keratinocytes 1 day after wounding. AChE appears to be functionally important for polarised cell migration, since an AChE antibody reduces substratum adhesion of fibroblasts, and slows wound healing in vitro as effectively as a beta1-integrin antibody. Moreover, elevation of AChE expression increases fibroblast wound healing independently of catalytic activity. Interestingly, AChE surface patches precisely co-localise with amyloid precursor protein and the extracellular matrix protein perlecan, but not focal adhesions or alpha-dystroglycan, and contain a high concentration of tyrosine phosphorylated proteins in spreading cells. These findings suggest that cell surface AChE, possibly in a novel signalling complex containing APP and perlecan, contributes to a generalised mechanism for polarised membrane protrusion and migration in all adherent cells.
Our study has shown that the Amaryllidaceae isocarbostyril narciclasine induces marked apoptosis-mediated cytotoxic effects in human cancer cells but not in normal fibroblasts by triggering the activation of the initiator caspases of the death receptor pathway (caspase-8 and caspase-10) at least in human MCF-7 breast and PC-3 prostate carcinoma cells. The formation of the Fas and death receptor 4 (DR4) death-inducing signaling complex was clearly evidenced in MCF-7 and PC-3 cancer cells. Caspase-8 was found to interact with Fas and DR4 receptors on narciclasine treatment. However, narciclasine-induced downstream apoptotic pathways in MCF-7 cells diverged from those in PC-3 cells, where caspase-8 directly activated effector caspases such as caspase-3 in the absence of any further release of mitochondrial proapoptotic effectors. In contrast, in MCF-7 cells, the apoptotic process was found to require an amplification step that is mitochondria-dependent, with Bid processing, release of cytochrome c, and caspase-9 activation. It is postulated that the high selectivity of narciclasine to cancer cells might be linked, at least in part, to this activation of the death receptor pathway. Normal human fibroblasts appear approximately 250-fold less sensitive to narciclasine, which does not induce apoptosis in these cells probably due to the absence of death receptor pathway activation.
Cardiomyocytes stop dividing after birth and postnatal heart growth is only achieved by increase in cell volume. In some species, cardiomyocytes undergo an additional incomplete mitosis in the first postnatal week, where karyokinesis takes place in the absence of cytokinesis, leading to binucleation. Proteins that regulate the formation of the actomyosin ring are known to be important for cytokinesis. Here we demonstrate for the first time that small GTPases like RhoA along with their downstream effectors like ROCK I, ROCK II and Citron Kinase show a developmental stage specific expression in heart, with high levels being expressed in cardiomyocytes only at stages when cytokinesis still occurs (i.e. embryonic and perinatal). This suggests that downregulation of many regulatory and cytoskeletal components involved in the formation of the actomyosin ring may be responsible for the uncoupling of cytokinesis from karyokinesis in rodent cardiomyocytes after birth. Interestingly, when the myocardium tries to adapt to the increased workload during pathological hypertrophy a re-expression of proteins involved in DNA synthesis and cytokinesis can be detected. Nevertheless, the adult cardiomyocytes do not appear to divide despite this upregulation of the cytokinetic machinery. The inability to undergo complete division could be due to the presence of stable, highly ordered and functional sarcomeres in the adult myocardium or could be because of the inefficiency of degradation pathways, which facilitate the division of differentiated embryonic cardiomyocytes by disintegrating myofibrils.
The fidelity of chromosome segregation depends on proper regulation of mitotic spindle behaviour. In anaphase, spindle stability is promoted by the dephosphorylation of cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) substrates, which results from Cdk inactivation and phosphatase activation. Few of the critical Cdk targets have been identified. Here, we identify the budding-yeast protein Fin1 (ref. 7) as a spindle-stabilizing protein whose activity is strictly limited to anaphase by changes in its phosphorylation state and rate of degradation. Phosphorylation of Fin1 from S phase to metaphase, by the cyclin-dependent kinase Clb5-Cdk1, inhibits Fin1 association with the spindle. In anaphase, when Clb5-Cdk1 is inactivated, Fin1 is dephosphorylated by the phosphatase Cdc14. Fin1 dephosphorylation targets it to the poles and microtubules of the elongating spindle, where it contributes to spindle integrity. A non-phosphorylatable Fin1 mutant localizes to the spindle before anaphase and impairs efficient chromosome segregation. As cells complete mitosis and disassemble the spindle, the ubiqutin ligase APC(Cdh1) targets Fin1 for destruction. Our studies illustrate how phosphorylation-dependent changes in the behaviour of Cdk1 substrates influence complex mitotic processes.
DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), which are generated by ionizing radiation (IR) and a range of other DNA damaging agents, are repaired by homologous recombination (HR) or non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ). Previous studies have shown that NHEJ in Saccharomyces cerevisiae requires the Yku70p-Yku80p heterodimer and a complex consisting of DNA Ligase IV, Lif1p and Nej1p. Here, we report that Nej1p is phosphorylated in response to DNA damage in a manner that relies on the DNA damage checkpoint kinases Mec1p, Rad53p and Dun1p. By using a mutational approach, we have identified a consensus Dun1p phosphorylation site in Nej1p, and mutation of conserved serine residues within it leads to decreased NHEJ efficiency. These data, together with previous findings that Rad55p--a protein involved in HR--is phosphorylated analogously, point to there being a broad signalling network connecting DNA damage checkpoint responses with the regulation of DNA DSB repair activities.
Phosphorylation of Tau protein and binding to microtubules is complex in neurons and was therefore studied in the less complicated model of humanized yeast. Human Tau was readily phosphorylated at pathological epitopes, but in opposite directions regulated by kinases Mds1 and Pho85, orthologues of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and cdk5, respectively (1). We isolated recombinant Tau-4R and mutant Tau-P301L from wild type, Delta mds1 and Delta pho85 yeast strains and measured binding to Taxol-stabilized mammalian microtubules in relation to their phosphorylation patterns. Tau-4R isolated from yeast lacking mds1 was less phosphorylated and bound more to microtubules than Tau-4R isolated from wild type yeast. Paradoxically, phosphorylation of Tau-4R isolated from kinase Pho85-deficient yeast was dramatically increased resulting in very poor binding to microtubules. Dephosphorylation promoted binding to microtubules to uniform high levels, excluding other modifications. Isolated hyperphosphorylated, conformationally altered Tau-4R completely failed to bind microtubules. In parallel to Tau-4R, we expressed, isolated, and analyzed mutant Tau-P301L. Total dephosphorylated Tau-4R and Tau-P301L bound to microtubules very similarly. Surprisingly, Tau-P301L isolated from all yeast strains bound to microtubules more extensively than Tau-4R. Atomic force microscopy demonstrated, however, that the high apparent binding of Tau-P301L was due to aggregation on the microtubules, causing their deformation and bundling. Our data explain the pathological presence of granular Tau aggregates in neuronal processes in tauopathies.
Non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) are the leading cause of cancer deaths in most developed countries. Targeting heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) expression and function, together with the induction of lysosomal membrane permeabilization (LMP), could overcome the multiple anti-cell death mechanisms evidenced in NSCLCs that are responsible for the failure of currently used chemotherapeutic drugs. Because cardenolides bind to the sodium pump, they affect multiple signaling pathways and thus have a number of marked effects on tumor cell behavior. The aim of the present study was to characterize in vitro and in vivo the antitumor effects of a new cardenolide (UNBS1450) on experimental human NSCLCs. UNBS1450 is a potent source of in vivo antitumor activity in the case of paclitaxel-and oxaliplatin-resistant subcutaneous human NCI-H727 and orthotopic A549 xenografts in nude mice. In vitro UNBS1450-mediated antitumor activity results from the induction of nonapoptotic cell death. UNBS1450 mediates the decrease of Hsp70 at both mRNA and protein levels, and this is at least partly due to UNBS1450-induced downregulation of NFAT5/TonEBP (a factor responsible for the transcriptional control of Hsp70). These effects were paralleled by the induction of LMP, as evidenced by acridine orange staining and immunofluorescence analysis for cathepsin B accumulation.
Heart growth in the embryo is achieved by division of differentiated cardiomyocytes. Around birth, cardiomyocytes stop dividing and heart growth occurs only by volume increase of the individual cells. Cardiomyocytes seem to lose their capacity for cytokinesis at this developmental stage. Septins are GTP-binding proteins that have been shown to be involved in cytokinesis from yeast to vertebrates. We wanted to determine whether septin expression patterns can be correlated to the cessation of cytokinesis during heart development. We found significant levels of expression only for SEPT2, SEPT6, SEPT7 and SEPT9 in heart, in a developmentally regulated fashion, with high levels in the embryonic heart, downregulation around birth and no detectable expression in the adult. In dividing embryonic cardiomyocytes, all septins localize to the cleavage furrow. We used drugs to probe for the functional interactions of SEPT2 in dividing embryonic cardiomyocytes. Differences in the effects on subcellular septin localization in cardiomyocytes were observed, depending whether a Rho kinase (ROCK) inhibitor was used or whether actin and myosin were targeted directly. Our data show a tight correlation of high levels of septin expression and the ability to undergo cytokinesis in cardiomyocytes. In addition, we were able to dissect the different contributions of ROCK signaling and the actomyosin cytoskeleton to septin localization to the contractile ring using cardiomyocytes as an experimental system.
Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli infection of intestinal epithelial cells leads to localized depletion of the microtubule cytoskeleton, an effect that is dependent on delivery of type III translocated effector proteins EspG and Orf3 (designated EspG2) to the site of depletion. Microtubule depletion involved disruption rather than displacement of microtubules.
We have used immunocytochemistry to demonstrate that the EAST protein in Drosophila, which forms an expandable nuclear endoskeleton at interphase, redistributes during mitosis to colocalize with the spindle matrix proteins, Megator and Skeletor. EAST and Megator also colocalize to the intranuclear space surrounding the chromosomes at interphase. EAST is a novel protein that does not have any previously characterized motifs or functional domains. However, we show by immunoprecipitation experiments that EAST is likely to molecularly interact with Megator which has a large NH2-terminal coiled-coil domain with the capacity for self assembly. On the basis of these findings, we propose that Megator and EAST interact to form a nuclear endoskeleton and as well are important components of the putative spindle matrix complex during mitosis.
In undisturbed cells, the MAPK-activated protein kinase Rck2 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a stable protein with a turnover time exceeding 60 min. However, we have found that Rck2 is subject to intracellular degradation after exposure of cells to Zn2+ concentrations of 5 mM or more. In high-zinc medium, most of the Rck2 pool is degraded within 5 min. This degradation is blocked by inhibiting the vacuolar proteolytic pathway with the protease inhibitor phenyl methyl sulphonyl fluoride or by mutation of the PEP4 gene. By contrast, blocking the proteasomal pathway with the inhibitor MG132 does not prevent Rck2 degradation upon addition of Zn2+, nor is degradation inhibited in the proteasomal mutations pre1 pre2, cim3, or cim5. The stability of Rck2 is not affected by any of the other stress conditions examined, or by growth rate. Possible mechanisms of the degradation of Rck2 under high zinc conditions, and its physiological significance, are discussed.
Transgenic mice overexpressing the P301L mutant human tau protein exhibit an accumulation of hyperphosphorylated tau and develop neurofibrillary tangles. The consequences of tau pathology were investigated here by proteomics followed by functional analysis. Mainly metabolism-related proteins including mitochondrial respiratory chain complex components, antioxidant enzymes, and synaptic proteins were identified as modified in the proteome pattern of P301L tau mice. Significantly, the reduction in mitochondrial complex V levels in the P301L tau mice revealed using proteomics was also confirmed as decreased in human P301L FTDP-17 (frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17) brains. Functional analysis demonstrated a mitochondrial dysfunction in P301L tau mice together with reduced NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase activity and, with age, impaired mitochondrial respiration and ATP synthesis. Mitochondrial dys-function was associated with higher levels of reactive oxygen species in aged transgenic mice. Increased tau pathology as in aged homozygous P301L tau mice revealed modified lipid peroxidation levels and the up-regulation of antioxidant enzymes in response to oxidative stress. Furthermore, P301L tau mitochondria displayed increased vulnerability toward beta-amyloid (Abeta) peptide insult, suggesting a synergistic action of tau and Abeta pathology on the mitochondria. Taken together, we conclude that tau pathology involves a mitochondrial and oxidative stress disorder possibly distinct from that caused by Abeta.
Budding yeast PDS5 is an essential gene in mitosis and is required for chromosome condensation and sister chromatid cohesion. Here we report that PDS also is required in meiosis. Pds5p localizes on chromosomes at all stages during meiotic cycle, except anaphase I. PDS5 plays an important role at first meiotic prophase. Failure in function of PDS5 causes premature separation of chromosomes. The loading of Pds5p onto chromosome requires the function of REC8, but the association of Rec8p with chromosome is independent of PDS5. Mutant analysis and live cell imaging indicate that PDS5 play a role in meiosis II as well.
We demonstrate a role for Qri2 in the essential DNA repair function of the Smc5/6 complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. We generated temperature-sensitive (ts) mutants in QRI2 and characterized their properties. The mutants arrest after S phase and prior to mitosis. Furthermore, the arrest is dependant on the Rad24 checkpoint, and is also accompanied by phosphorylation of the Rad53 checkpoint effector kinase. The mutants also display genome instability and are sensitive to agents that damage DNA. Two-hybrid screens reveal a physical interaction between Qri2 and proteins that are non-Smc elements of the Smc5/6 DNA repair complex, which is why we propose the name NSE4 for the open reading frame previously known as QRI2. A key role for Nse4 in Smc5/6 function is likely, as overexpressing known subunits of the Smc5/6 complex suppresses nse4(ts) cell cycle arrest. The nse4(ts) growth arrest is non-lethal and unlike the catastrophic nuclear fragmentation phenotype of smc6(ts) mutants, the nucleus remains intact; replicative intermediates and sheared DNA are not detected. This could imply a role for Nse4 in maintenance of higher order chromosome structure.
Centrioles organize pericentriolar material to form centrosomes and also template the formation of cilia. Despite the importance of centrioles in dividing and differentiated cells, their assembly remains poorly understood at a molecular level. Here, we develop a fluorescence microscopy-based assay for centriole assembly in the 1-cell stage C. elegans embryo. We use this assay to characterize SAS-6, a centriolar protein that we identified based on its requirement for centrosome duplication. We show that SAS-6, a member of a conserved metazoan protein family, is specifically required for new centriole assembly, a result we confirm by electron microscopy. We further use the centriole assembly assay to examine the roles of three pericentriolar material proteins: SPD-5, the kinase aurora-A, and gamma-tubulin. Our results suggest that the pericentriolar material promotes daughter centriole formation by concentrating gamma-tubulin around the parent centriole. Thus, both centriolar and pericentriolar material proteins contribute to centriole assembly.
Pure hereditary spastic paraplegia is characterized by length-dependent degeneration of the distal ends of long axons. Mutations in spastin are the most common cause of the condition. We set out to investigate the function of spastin using a yeast two-hybrid approach to identify interacting proteins. Using full-length spastin as bait, we identified CHMP1B, a protein associated with the ESCRT (endosomal sorting complex required for transport)-III complex, as a binding partner. Several different approaches confirmed the physiological relevance of the interaction in mammalian cells. Epitope-tagged CHMP1B and spastin showed clear cytoplasmic co-localization in Cos-7 and PC12 cells. CHMP1B and spastin interacted specifically in vitro and in vivo in beta-lactamase protein fragment complementation assays, and spastin co-immunoprecipitated with CHMP1B. The interaction was mediated by a region of spastin lying between residues 80 and 196 and containing a microtubule interacting and trafficking domain. Expression of epitope-tagged CHMP1B in mammalian cells prevented the development of the abnormal microtubule phenotype associated with expression of ATPase-defective spastin. These data point to a role for spastin in intracellular membrane traffic events and provide further evidence to support the emerging recognition that defects in intracellular membrane traffic are a significant cause of motor neuron pathology.
We have used immunocytochemistry and cross-immunoprecipitation analysis to demonstrate that Megator (Bx34 antigen), a Tpr ortholog in Drosophila with an extended coiled-coil domain, colocalizes with the putative spindle matrix proteins Skeletor and Chromator during mitosis. Analysis of P-element mutations in the Megator locus showed that Megator is an essential protein. During interphase Megator is localized to the nuclear rim and occupies the intranuclear space surrounding the chromosomes. However, during mitosis Megator reorganizes and aligns together with Skeletor and Chromator into a fusiform spindle structure. The Megator metaphase spindle persists in the absence of microtubule spindles, strongly implying that the existence of the Megator-defined spindle does not require polymerized microtubules. Deletion construct analysis in S2 cells indicates that the COOH-terminal part of Megator without the coiled-coil region was sufficient for both nuclear as well as spindle localization. In contrast, the NH2-terminal coiled-coil region remains in the cytoplasm; however, we show that it is capable of assembling into spherical structures. On the basis of these findings we propose that the COOH-terminal domain of Megator functions as a targeting and localization domain, whereas the NH2-terminal domain is responsible for forming polymers that may serve as a structural basis for the putative spindle matrix complex.
FtsZ is a filament-forming protein that assembles into a ring at the division site of prokaryotic cells. As FtsZ and tubulin share several biochemical and structural similarities, FtsZ is regarded as the ancestor of tubulin. Chloroplasts--the descendants of endosymbiotic bacteria within plant cells--also harbour FtsZ. In contrast to eubacteria, plants have several different FtsZ isoforms. So far, these isoforms have only been implicated with filamentous structures, rings and networks, inside chloroplasts. Here, we demonstrate that a novel FtsZ isoform in the moss Physcomitrella patens is located not only in chloroplasts but also in the cytoplasm, assembling into rings in both cell compartments. These findings comprise the first report on cytosolic localization of a eukaryotic FtsZ isoform, and indicate that this protein might connect cell and organelle division at least in moss.
Set1p methylates lysine 4 of histone H3 and can activate transcription by recruiting the chromatin-remodeling factor Isw1p. In addition, Lys-4-methylated H3 is required for maintenance of silencing at the telomeres, rDNA, and HML locus in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The molecular mechanism underlying the role of Set1p in silencing is not known. Here we report that euchromatic methylation of H3 Lys-4 is necessary to maintain silencing at specific heterochromatic sites. Inactivation of Set1p catalytic activity or mutation of H3 Lys-4 leads to decreased binding of the silent information regulator Sir3p at heterochromatic sites. Concomitantly, there is an increase in the amount of Sir3p bound to genes located in subtelomeric regions. Consistent with this result is the finding that in vitro, Sir3p preferentially binds histone H3 tails when methylation is absent at H3 Lys-4, a situation found in heterochromatin. The inability of Sir3p to bind methylated H3 Lys-4 tails suggests a model whereby H3 Lys-4 methylation prevents Sir3p association at euchromatic sites and therefore concentrates Sir3p at unmodified, heterochromatic regions of the genome.
Mechanisms that coordinate cell growth with division are thought to determine the timing of initiation of cell division and to limit overall cell proliferation. To identify genes involved in this process in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, we describe a method that does not rely on cell size alterations or resistance to pheromone. Instead, our approach was based on the cell surface deposition of the Flo1p protein in cells having passed START. We found that over-expression of HXT11 (which encodes a plasma membrane transporter), PPE1 (coding for a protein methyl esterase), or SIK1 (which encodes a protein involved in rRNA processing) shortened the duration of the G1 phase of the cell cycle, prior to the initiation of DNA replication. In addition, we found that, although SIK1 was not part of a mitotic checkpoint, SIK1 over-expression caused spindle orientation defects and sensitized G2/M checkpoint mutant cells. Thus, unlike HXT11 and PPE1, SIK1 over-expression is also associated with mitotic functions. Overall, we used a novel enrichment approach and identified genes that were not previously associated with cell cycle progression. This approach can be extended to other organisms.
The reversible phosphorylation of serine and threonine residues N-terminal to proline (pSer/Thr-Pro) is an important signaling mechanism in the cell. The pSer/Thr-Pro moiety exists in the two distinct cis and trans conformations, whose conversion is catalyzed by the peptidyl-prolyl isomerase (PPIase) Pin1. Among others, Pin1 binds to the phosphorylated C-terminal domain (CTD) of the largest subunit of the RNA polymerase II, but the biochemical and functional relevance of this interaction is unknown. Here we confirm that the CTD phosphatase Fcp1 can suppress a Pin1 mutation in yeast. Furthermore, this genetic interaction requires the phosphatase domain as well as the BRCT domain of Fcp1, suggesting a critical role of the Fcp1 localization. Based on these observations, we developed a new in vitro assay to analyze the CTD dephosphorylation by Fcp1 that uses only recombinant proteins and mimics the in vivo situation. This assay allows us to present strong evidence that Pin1 is able to stimulate CTD dephosphorylation by Fcp1 in vitro, and that this stimulation depends on Pin1's PPIase activity. Finally, Pin1 significantly increased the dephosphorylation of the CTD on the Ser(5)-Pro motif, but not on Ser(2)-Pro in yeast, which can be explained with Pin1's substrate specificity. Together, our results indicate a new role for Pin1 in the regulation of CTD phosphorylation and present a further example for prolyl isomerization-dependent protein dephosphorylation.
Background: Flavopiridol a semisynthetic flavone that inhibits cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) and has growth-inhibitory activity and induces a blockade of cell-cycle progression at G1-phase and apoptosis in numerous human tumor cell lines and is currently under investigation in phase II clinical trials. Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are comprised of subpopulation of cells in tumors that have been proposed to be responsible for recurrence and resistance to chemotherapy. The aim of the present study was to investigate the effects of flavopiridol in cancer stem cell cytoskeleton, cell adhesion, and epithelial to mesenchymal transition in CSCs.
Methods: The cells were treated with flavopiridol to determine the inhibitory effect. Cell viability and proliferation were determined by using the WST-1 assay. Caspase activity and immunofluorescence analyses were performed for the evaluation of apoptosis, cell cytoskeleton, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers. The effects of flavopiridol on the cell cycle were also evaluated. Flow cytometric analysis was used to detect the percentages of CSCs subpopulation. We analyzed the gene expression patterns to predict cell cycle and cell cytoskeleton in CSCs by RT-PCR.
Results: Flavopiridol-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis at the IC50 dose, resulting in a significant increase expression of caspases activity. Cell cycle analyses revealed that flavopiridol induces G1 phase cell cycle arrest. Flavopiridol significantly decreased the mRNA expressions of the genes that regulate the cell cytoskeleton and cell cycle components and cell motility in CSCs.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that Flavopiridol has activity against lung CSCs and may be effective chemotherapeutic molecule for lung cancer treatment.
Background: E-cadherin is an adherens junction protein that forms homophilic intercellular contacts in epithelial cells while also interacting with the intracellular cytoskeletal networks. It has roles including establishment and maintenance of cell polarity, differentiation, migration and signalling in cell proliferation pathways. Its downregulation is commonly observed in epithelial tumours and is a hallmark of the epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT).
Methods: To improve our understanding of how E-cadherin loss contributes to tumorigenicity, we investigated the impact of its elimination from the non-tumorigenic breast cell line MCF10A. We performed cell-based assays and whole genome RNAseq to characterize an isogenic MCF10A cell line that is devoid of CDH1 expression due to an engineered homozygous 4 bp deletion in CDH1 exon 11.
Results: The E-cadherin-deficient line, MCF10A CDH1-/- showed subtle morphological changes, weaker cell-substrate adhesion, delayed migration, but retained cell-cell contact, contact growth inhibition and anchorage-dependent growth. Within the cytoskeleton, the apical microtubule network in the CDH1-deficient cells lacked the radial pattern of organization present in the MCF10A cells and F-actin formed thicker, more numerous stress fibres in the basal part of the cell. Whole genome RNAseq identified compensatory changes in the genes involved in cell-cell adhesion while genes involved in cell-substrate adhesion, notably ITGA1, COL8A1, COL4A2 and COL12A1, were significantly downregulated. Key EMT markers including CDH2, FN1, VIM and VTN were not upregulated although increased expression of proteolytic matrix metalloprotease and kallikrein genes was observed.
Conclusions: Overall, our results demonstrated that E-cadherin loss alone was insufficient to induce an EMT or enhance transforming potential in the non-tumorigenic MCF10A cells but was associated with broad transcriptional changes associated with tissue remodelling.
Background: Class III beta-tubulin overexpression is a marker of resistance to microtubule disruptors in vitro, in vivo and in the clinic for many cancers, including breast cancer. The aims of this study were to develop a new model of class III beta-tubulin expression, avoiding the toxicity associated with chronic overexpression of class III beta-tubulin, and study the efficacy of a panel of clinical and pre-clinical drugs in this model.
Methods: MCF-7 (ER+ve) and MDA-MB-231 (ER-ve) were either transfected with pALTER-TUBB3 or siRNA-tubb3 and 24 h later exposed to test compounds for a further 96 h for proliferation studies. RT-PCR and immunoblotting were used to monitor the changes in class III beta-tubulin mRNA and protein expression.
Results: The model allowed for subtle changes in class III beta-tubulin expression to be achieved, which had no direct effect on the viability of the cells. Class III beta-tubulin overexpression conferred resistance to paclitaxel and vinorelbine, whereas downregulation of class III beta-tubulin rendered cells more sensitive to these two drugs. The efficacy of the colchicine-site binding agents, 2-MeOE2, colchicine, STX140, ENMD1198 and STX243 was unaffected by the changes in class III beta-tubulin expression.
Conclusion: These data indicate that the effect of class III beta-tubulin overexpression may depend on where the drug's binding site is located on the tubulin. Therefore, this study highlights for the first time the potential key role of targeting the colchicine-binding site, to develop new treatment modalities for taxane-refractory breast cancer.
Background: The nasal cavity of all vertebrates houses multiple chemosensors, either innervated by the Ist (olfactory) or the Vth (trigeminal) cranial nerve. Various types of receptor cells are present, either segregated in different compartments (e.g. in rodents) or mingled in one epithelium (e.g. fish). In addition, solitary chemosensory cells have been reported for several species. Alligators which seek their prey both above and under water have only one nasal compartment. Information about their olfactory epithelium is limited. Since alligators seem to detect both volatile and water-soluble odour cues, I tested whether different sensory cell types are present in the olfactory epithelium.
Results: Electron microscopy and immunocytochemistry were used to examine the sensory epithelium of the nasal cavity of the American alligator. Almost the entire nasal cavity is lined with olfactory (sensory) epithelium. Two types of olfactory sensory neurons are present. Both types bear cilia as well as microvilli at their apical endings and express the typical markers for olfactory neurons. The density of these olfactory neurons varies along the nasal cavity. In addition, solitary chemosensory cells innervated by trigeminal nerve fibres, are intermingled with olfactory sensory neurons. Solitary chemosensory cells express components of the PLC-transduction cascade found in solitary chemosensory cells in rodents.
Conclusion: The nasal cavity of the American alligator contains two different chemosensory systems incorporated in the same sensory epithelium: the olfactory system proper and solitary chemosensory cells. The olfactory system contains two morphological distinct types of ciliated olfactory receptor neurons.
Background: Wnt factors are a large family of signaling molecules that play important roles in the regulation of cell fate specification, tissue polarity and cell movement. In the nervous system, Wnts also regulates the formation of neuronal connection acting as retrograde signals that regulate the remodeling of the axons prior to the assembly of the presynaptic apparatus. The scaffold protein Dishevelled (Dvl) mimics the effect of Wnt on the neuronal cytoskeleton by increasing the number of stable microtubule along the axon shaft and inducing the formation of looped microtubules (MT) at enlarged growth cones. A divergent Wnt-Dvl canonical pathway which bifurcates downstream of Gsk3beta regulates MT dynamics.
Results: Here we show that the Wnt pathway also activates c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) to regulate MT stabilization. Although in the Wnt planar cell polarity (PCP) pathway, JNK lays downstream of Rho GTPases, these GTPases are not required for Wnt-mediated MTs stability. Epistatic analyses and pharmacological studies suggest that the Wnt-Dvl signalling regulates the dynamic of the cytoskeleton through two different pathways that lead to inhibition of Gsk3beta and activation of JNK in the same cell.
Conclusion: We demonstrate a novel role for JNK in Wnt-mediated MT stability. Wnt-Dvl pathway increases MT stability through a transcription independent mechanism that requires the concomitant inhibition of Gsk3beta and activation of JNK. These studies demonstrate that Wnts can simultaneously activate different signalling pathways to modulate cytoskeleton dynamics.
![Western Blot - Anti-alpha Tubulin Antibody [ARC2486] (A308887) - Antibodies.com](https://cdn.antibodies.com/image/catalog/308/A308887_1.jpg?profile=product_alternative)
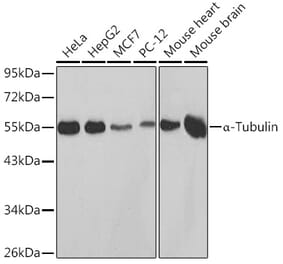
![Immunocytochemistry - Anti-alpha Tubulin Antibody [RM113] (A121300) - Antibodies.com](https://cdn.antibodies.com/image/catalog/121/A121506_1.png?profile=product_alternative)
![Western Blot - Anti-alpha Tubulin (acetyl Lys40) Antibody [RM318] (A121247) - Antibodies.com](https://cdn.antibodies.com/image/catalog/121/A121247_1.png?profile=product_alternative)
![Immunohistochemistry - Anti-alpha Tubulin Antibody [TUBA/3038] (A250228) - Antibodies.com](https://cdn.antibodies.com/image/catalog/250/A250228_1.jpg?profile=product_alternative)
![Immunohistochemistry - Anti-alpha Tubulin Antibody [TUBA/3038] - BSA and Azide free (A253408) - Antibodies.com](https://cdn.antibodies.com/image/catalog/253/A253408_1.jpg?profile=product_alternative)
![Western Blot - Anti-alpha Tubulin Antibody [ARC2486] (A308887) - Antibodies.com](https://cdn.antibodies.com/image/catalog/308/A308887_1.jpg?profile=product_alternative)

![Immunocytochemistry - Anti-alpha Tubulin Antibody [RM113] (A121300) - Antibodies.com](https://cdn.antibodies.com/image/catalog/121/A121506_1.png?profile=product_alternative)
![Western Blot - Anti-alpha Tubulin (acetyl Lys40) Antibody [RM318] (A121247) - Antibodies.com](https://cdn.antibodies.com/image/catalog/121/A121247_1.png?profile=product_alternative)
![Immunohistochemistry - Anti-alpha Tubulin Antibody [TUBA/3038] (A250228) - Antibodies.com](https://cdn.antibodies.com/image/catalog/250/A250228_1.jpg?profile=product_alternative)
![Immunohistochemistry - Anti-alpha Tubulin Antibody [TUBA/3038] - BSA and Azide free (A253408) - Antibodies.com](https://cdn.antibodies.com/image/catalog/253/A253408_1.jpg?profile=product_alternative)
![Immunocytochemistry - Anti-alpha Tubulin Antibody [YOL1/34] (A254435) - Antibodies.com](https://cdn.antibodies.com/image/catalog/254/A254436_1.jpg?profile=product_top)
![Immunocytochemistry - Anti-alpha Tubulin Antibody [YOL1/34] (A254435) - Antibodies.com](https://cdn.antibodies.com/image/catalog/254/A254436_1.jpg?profile=product_top_thumb)
![Immunocytochemistry - Anti-alpha Tubulin Antibody [TU-01] (A86726) - Antibodies.com](https://cdn.antibodies.com/image/catalog/86/A86726_840.jpg?profile=product_alternative)
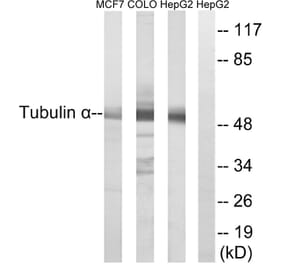
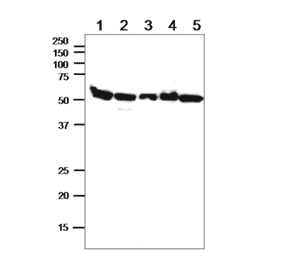
![Immunocytochemistry - Anti-alpha Tubulin Antibody [YOL1/34] (A254435) - Antibodies.com](https://cdn.antibodies.com/image/catalog/254/A254436_1.jpg?profile=product_image)


![Immunoprecipitation - Anti-alpha Tubulin Antibody [TU-16] (A86708) - Antibodies.com](https://cdn.antibodies.com/image/catalog/86/A86709_829.jpg?profile=product_alternative)
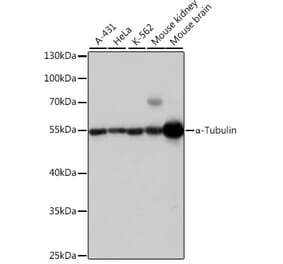
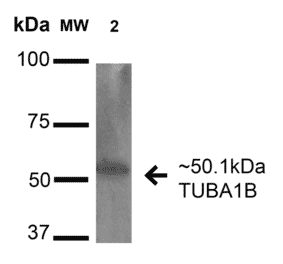
![Western Blot - Anti-alpha Tubulin Antibody [TU-02] (A86721) - Antibodies.com](https://cdn.antibodies.com/image/catalog/86/A86724_838.jpg?profile=product_alternative)